Research Status of Pegmatite-hosted Li Deposits and Their Exploration Prospect in West China
-
摘要:
锂现为全球战略性关键金属矿产,花岗伟晶岩型锂矿是锂资源的重要类型之一,也是当前国际矿床学的研究热点。花岗伟晶岩划分为LCT(Li–Cs–Ta)、NYF(Nb–Y–F)及二者混合的LCT+NYF型,其中LCT型伟晶岩富集稀有元素Li、Rb、Cs、Be、Ga、Sn、Ta、Nb及B、P、F等助熔剂,通常与伸展背景下的晚造山和造山后阶段过铝质S型花岗岩具有成因联系。笔者分析了全球伟晶岩型锂矿床的时空分布特征,发现锂矿成矿事件主要发生在超大陆会聚造山作用的中晚期。研究表明中国花岗伟晶岩型锂矿空间分布相对集中,主要分布在9个锂成矿带,成矿期以三叠纪为主。花岗质岩浆结晶分异和下地壳物质低程度的部分熔融是伟晶岩两种主要的形成方式。稀有金属伟晶岩的成矿机制主要有分离结晶作用、岩浆不混溶、超临界流体和组成带状纯化。总结分析了中国西部西昆仑、川西松潘–甘孜、阿尔泰等3个典型伟晶岩型锂矿带的的成矿特点、分布特征、研究进展及找矿前景,并提出了构造–岩浆–变质–成矿的耦合关系是制约锂成矿过程和富集规律的关键科学问题。
Abstract:Lithium has become an important strategic critical metal in the world, and the granitic pegmatite type lithium deposit is one of the important types of lithium resources, which is also a popular interest in the current international ore deposit research. The granitic pegmatites are classified into LCT (Li–Cs–Ta), NYF (Nb–Y–F) and mixed LCT+NYF type. The LCT type pegmatites are characterized by enrichment of rare elements Li, Rb, Cs, Be, Ga, Sn, Ta>Nb and fluxing components B, P, F, usually related to late orogenic and post–orogenic peraluminous S–type granites in extensional background. In this paper, we review the temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of pegmatite type lithium deposits in the world. It is noted that the lithium mineralization events mainly occurred in the middle and late period of convergent orogeny associated with the supercontinent assembly. The study shows that the spatial distribution of granitic pegmatite lithium deposits in China is relatively concentrated, mainly distributed in nine lithium metallogenic belts, of which the main mineralization period is Triassic. Fractional crystallization of granitic magma and partial melting of lower crust material are the two significant formation modes of pegmatites. The four metallogenic mechanism of rare metal pegmatite mainly include fractional crystallization, magmatic immiscibility, supercritical fluids and constitutional zone refining (CZR). We summarize the metallogenic characteristics, distribution characteristics, research progress and exploration prospect of the three typical pegmatite type lithium metallogenic belts, West Kunlun, Songpan–Ganze and Altay, in western China. The coupling relationship of structure–magmatism–metamorphism–mineralization is the key scientific problem that restricts the mineralization process and enrichment regularity of lithium.
-
锂是战略性新兴产业发展的关键性矿产资源(王登红,2019;毛景文等,2019;翟明国等,2019)。锂作为自然界最轻的金属元素,被广泛应用于冶金工业、轻工业纺织、电子技术、医药生理、国防尖端工业、原子能工业、新型清洁优势能源等领域,被誉为“白色石油”“工业味精”“高能金属”“21世纪的能源金属” (李建康等,2014;许志琴等,2018)。中国锂资源对外依存度非常高,已接近80%(翟明国等,2021)。随着锂电池、新能源汽车、可控核聚变等领域的快速发展,锂已成为未来国家新能源战略的重大需求。作为新一轮战略性矿产找矿突破行动36种战略性矿产之一,锂已成为现今找矿勘查和成矿研究的热点。
锂矿床主要的工业类型包括卤水型和硬岩型,卤水型可分为盐湖卤水型和地下卤水型,硬岩型又可分为伟晶岩型和花岗岩型,伟晶岩型锂矿是锂资源的主要来源之一(Kesler et al.,2012)。前人对稀有金属伟晶岩的成因及锂的富集成矿机制进行了大量的研究工作,取得了一系列重要成果(Černý et al.,2012;王瑞江等,2015;Thomas et al.,2016;London,2018;李建康等,2021)。笔者在系统总结前人成果的基础上,介绍了伟晶岩型锂矿床的类型及分布,探讨并分析了成矿伟晶岩的物质来源及伟晶岩型锂矿床的成因机制,总结了中国西部主要伟晶岩型锂成矿带的地质特征与成矿规律,剖析其找矿前景,以期为中国锂等稀有金属矿床研究及找矿勘查提供参考。
1. 伟晶岩型锂矿床的类型及分布
1.1 花岗伟晶岩的定义及类型划分
花岗伟晶岩是一类重要的火成岩,通常具有花岗质组成,以极度粗粒且变化的颗粒大小,或以大量骸晶、文象结构或其他强烈定向生长习性而区别于其他火成岩,并以矿物共生组合明显的空间分带为特征(London,2008,2014,2018)。
根据岩石成因及稀有金属成矿元素的组成特征,Černý(1991a,1992)、Černý 等(2005)把稀有金属花岗伟晶岩划分为LCT(富集Li–Cs–Ta)、NYF(富集Nb–Y–F)及二者混合的LCT+NYF型(表1)。LCT型伟晶岩富集稀有元素Li、Rb、Cs、Be、Ga、Sn、Ta>Nb及B、P、F等助熔剂,具过铝质S型花岗岩的特征,起源于大洋沉积物(主要为黑色页岩)的部分熔融,通常形成于伸展背景下的晚造山和造山后阶段,少数形成于同造山阶段。LCT型伟晶岩常具有典型的内部结构分带及矿物成分分带,从脉体外部向内部依次可发育边缘带(Border zone)、外部带(Wall zone)、中间带(Intermediate zone)和核部带(Core zone)。NYF型伟晶岩富集Nb>Ta、Ti、Y、REE、Zr、Th、U及F,具有次铝质–准铝质属性,主要与非造山或板内的A型花岗岩具有成因联系,NYF型伟晶岩通常表现出无或较弱的内部分带。LCT+NYF型稀有金属伟晶岩兼具LCT与NYF两种类型伟晶岩的特点,但这类伟晶岩研究较少,全球也仅有少量案例报道。相较于NYF型伟晶岩,LCT型伟晶岩分布广泛,在数量上远超过NYF型伟晶岩,前人所说的稀有金属花岗伟晶岩,一般均指LCT型伟晶岩。由于该分类方案建立了与花岗岩的联系,同时能够指示相关伟晶岩的形成机制和大地构造背景,因此为大多数学者所接受。
表 1 花岗伟晶岩的分类及特征表(据Černý et al.,2005)Table 1. Petrogenetic classification and characteristics of granitic pegmatites类型 地球化学特征 伟晶岩组成 内部岩相结构分带 相关花岗岩 潜在的母体花岗岩性质 源岩 LCT型 Li、Rb、Cs、Be、
Sn、Ga、Ta>Nb,
(B、P、F)过铝质–次铝质 岩相分带显著 (同造山)–晚造山–(非造山);成分主要是不均匀 过铝质S, I或混合S+I型 未亏损LCT元素的中–上地壳表壳岩石和基底片麻岩 NYF型 Nb>Ta、Ti、Y、
Sc、REE、Zr、
Th、U及F次铝质–准铝质(–亚碱性) 无–弱的岩相分带 (同造山、晚造山、后造山)–主要为非造山;成分准均匀 (过铝质)–次铝质和准铝质A和I型 亏损LCT元素的中–下地壳麻粒岩,新生花岗岩,地幔物质交代的地壳 LCT+NYF
混合型混合的 次铝质–中等过铝质 出现岩相分带 (后造山)–非造山;成分不均匀 次铝质–弱过铝质 混合的岩石源区;受NYF花岗岩浆同化的上地壳 1.2 伟晶岩型锂矿床在全球的分布
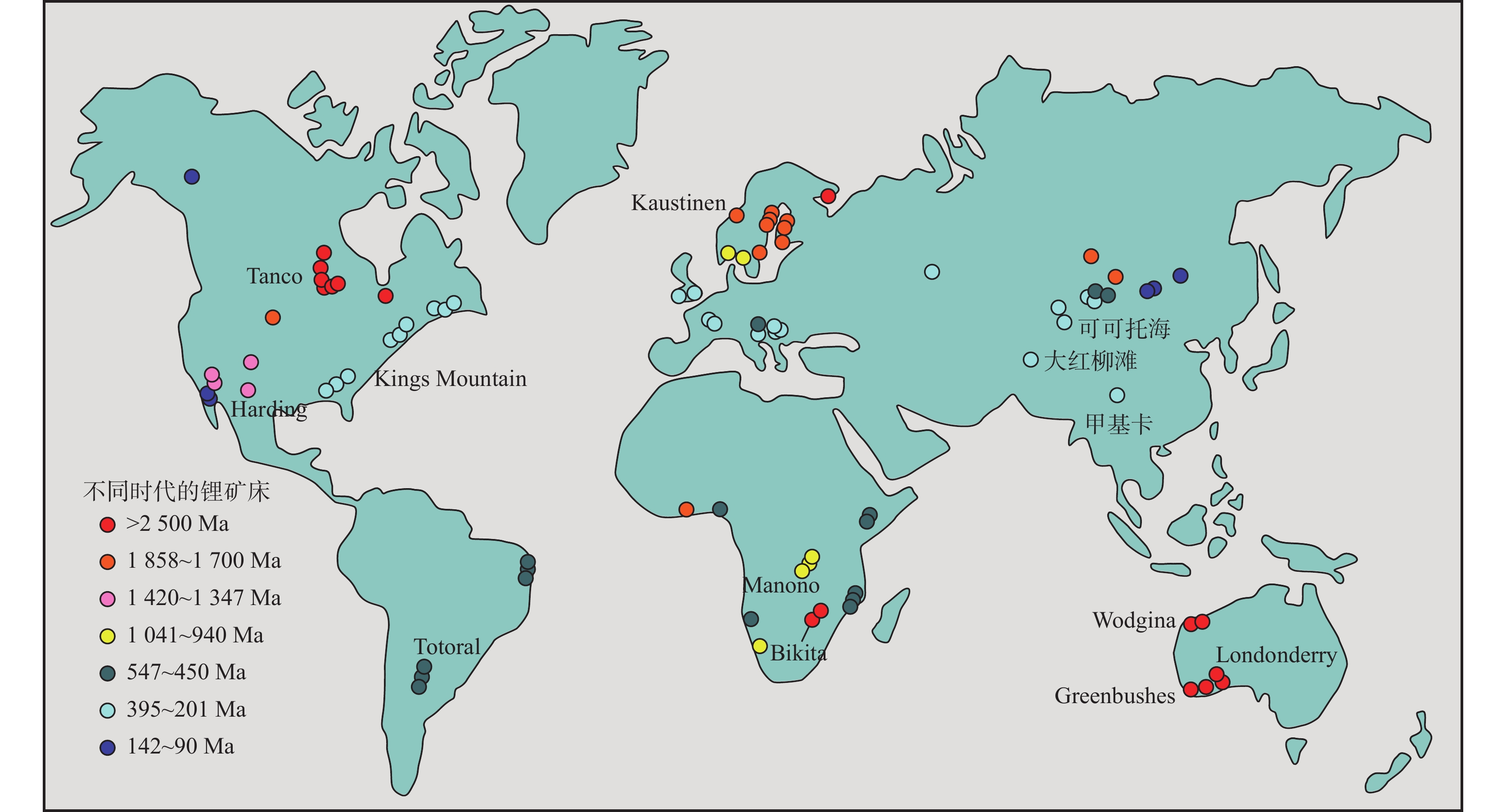
花岗伟晶岩型锂矿床主要分布于澳大利亚、北美、津巴布韦、中国、南美、北欧、西伯利亚等地,著名的矿床有津巴布韦克拉通的Bikita,西澳Pilbara克拉通的Wodgina,西澳Yilgarn克拉通的Greenbushes、Londonderry,加拿大北部的Tanco,美国北卡罗来纳的Kings Mountain,芬兰西部的Kaustinen,西伯利亚的东萨彦,非洲Congon克拉通的Manono,南美Famatinian造山带的Totoral,中国的可可托海、大红柳滩、甲基卡等。全球伟晶岩型锂矿在时空分布和构造背景方面具有明显的不均一性(陈衍景等,2021)。在南半球,伟晶岩型锂矿床集中分布于非洲中南部、澳洲西部及南美洲中南部,形成时代主要为前寒武纪,其次为早古生代,晚古生代及以后矿床分布较少。北半球的欧亚大陆和北美大陆的伟晶岩型锂矿床主要分布于中南部,形成时代与南半球正好相反,主要形成于晚古生代及之后,前寒武纪相对较少(图1)。
![]() 图 1 全球伟晶岩型锂矿床时空分布图(据陈衍景等,2021修改)Figure 1. The temporal and spatial distribution map of pegmatite–type Li deposits in the world
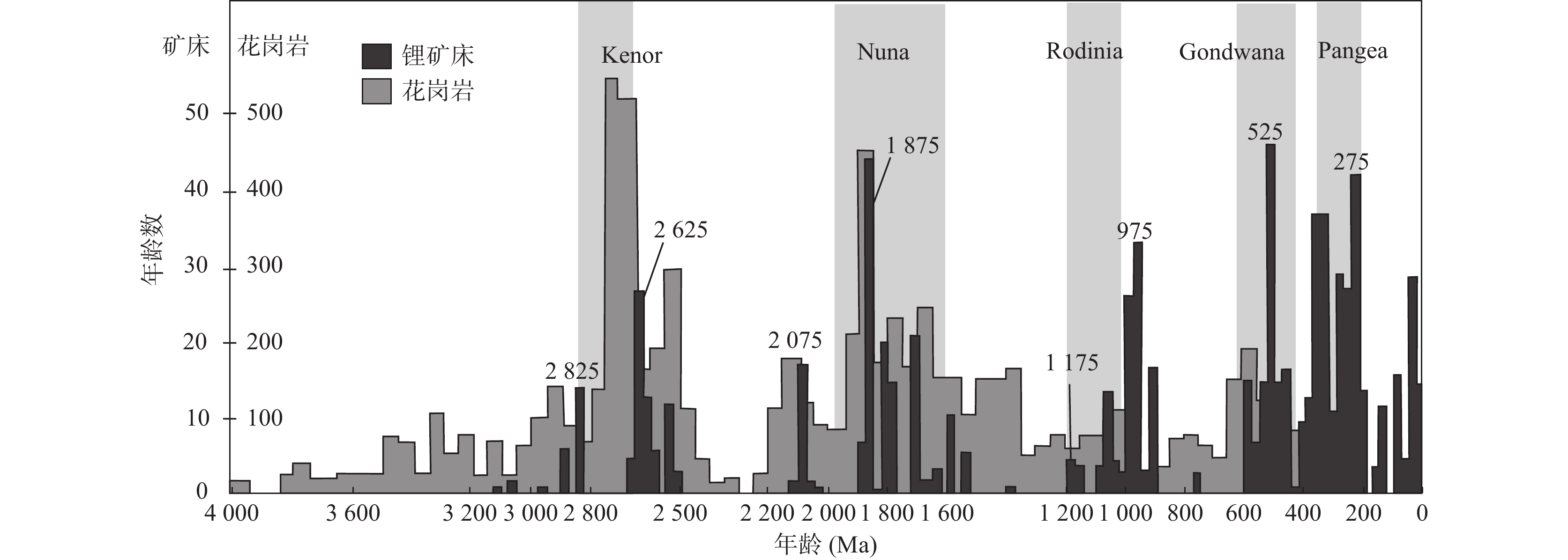
图 1 全球伟晶岩型锂矿床时空分布图(据陈衍景等,2021修改)Figure 1. The temporal and spatial distribution map of pegmatite–type Li deposits in the world在全球范围内,伟晶岩型锂矿形成时间与碰撞造山引起的超级大陆拼贴时间具有耦合关系。伟晶岩型锂矿形成峰值时间分别为2 825 Ma、2 625 Ma、2 075 Ma、1 875 Ma、975 Ma、525 Ma、275 Ma(Dittrich et al.,2019;陈衍景等,2021)。前人统计显示,全球LCT伟晶岩的出现频率及时代分布,与Kenor、Nuna、Rodinia、Gondwana、Pangea等超大陆聚合事件相伴随(图2),伟晶岩型锂矿形成于超大陆会聚造山作用的中晚期,滞后于构造变形。显然,国外著名的伟晶岩型锂矿床多形成于前寒武纪,而近年研究表明,三叠纪是中国伟晶岩型锂矿的重要成矿期(张辉等,2021)。印支地块与扬子、塔里木–华北陆块碰撞,印度与欧亚大陆碰撞,在中国形成了三叠纪的松潘–甘孜–西昆仑巨型伟晶岩型锂矿带和潜力巨大的新近纪与淡色花岗岩相关的喜马拉雅花岗–伟晶岩稀有金属成矿带,而西方学者对此还没有足够的重视。
1.3 伟晶岩型锂矿床在中国的分布
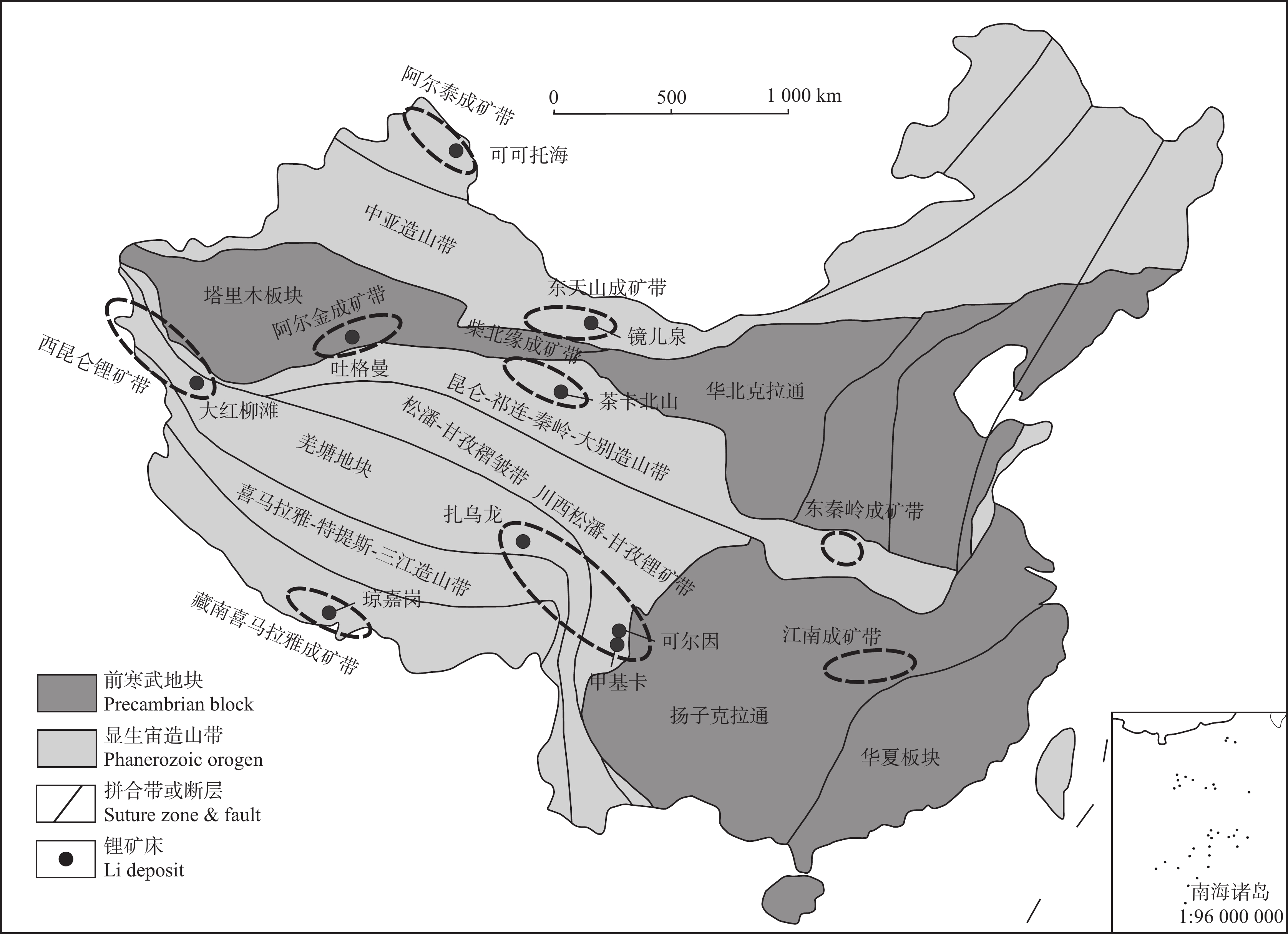
中国花岗伟晶岩型锂矿资源十分丰富,主要分布于中国西部的新疆与四川2地。其在空间上具有明显的成带集中分布的特点(图3),主要分布于阿尔泰、西昆仑–喀喇昆仑、川西松潘–甘孜、东天山、东秦岭、阿尔金、柴北缘、江南及藏南喜马拉雅锂铍等稀有金属成矿带。著名的矿床有阿尔泰成矿带的可可托海、卡鲁安,西昆仑–喀喇昆仑成矿带的大红柳滩–白龙山、川西松潘–甘孜成矿带的甲基卡、李家沟。中国伟晶岩型锂矿形成时代主要为三叠纪,阿尔金一带伟晶岩型锂矿形成于奥陶纪,江南成矿带幕阜山一带稀有金属矿床形成于燕山期,阿尔泰锂成矿带有泥盆—石炭纪、二叠纪、三叠纪和侏罗纪4个成矿期次,其中三叠纪是成岩成矿的主峰期(表2)。
![]() 图 3 中国主要伟晶岩型锂矿床及成矿带分布图(底图据毛景文等,2019)Figure 3. The sketch map of major pegmatite–type Li deposits and metallogenic belts in China
图 3 中国主要伟晶岩型锂矿床及成矿带分布图(底图据毛景文等,2019)Figure 3. The sketch map of major pegmatite–type Li deposits and metallogenic belts in China2. 伟晶岩型锂矿床物质来源及成因机制
2.1 成矿伟晶岩的物质来源及成岩方式
成矿花岗伟晶岩的源岩一般认为均为变质沉积岩系,变沉积岩中含较多的黏土矿物及云母类矿物,Li和其他稀有金属(如Be、Rb、Cs、Nb、Ta)及挥发性元素(B、F)在这些矿物中高度相容(London et al.,2017),有利于这些元素的预富集。这些源岩在相对富H2O条件下熔融时,稀有金属元素及助熔组分易于迁移,并被萃取至熔体中,最终分异演化形成相对富集稀有金属元素以及助熔剂的花岗质熔体,进一步演化形成各种类型的伟晶岩(London,2018)。
关于花岗伟晶岩的岩石成因,长期存在2种争议性的观点,目前一般认为花岗伟晶岩岩浆为花岗质岩浆结晶分异形成的富水残余岩浆(London,1986,2005;London et al.,2002;Simmons et al.,2008;Černý et al.,2012),也有部分学者认为花岗伟晶岩岩浆形成于下地壳物质低程度的部分熔融(Martin et al.,2005;Shaw et al.,2016),即深熔成因。
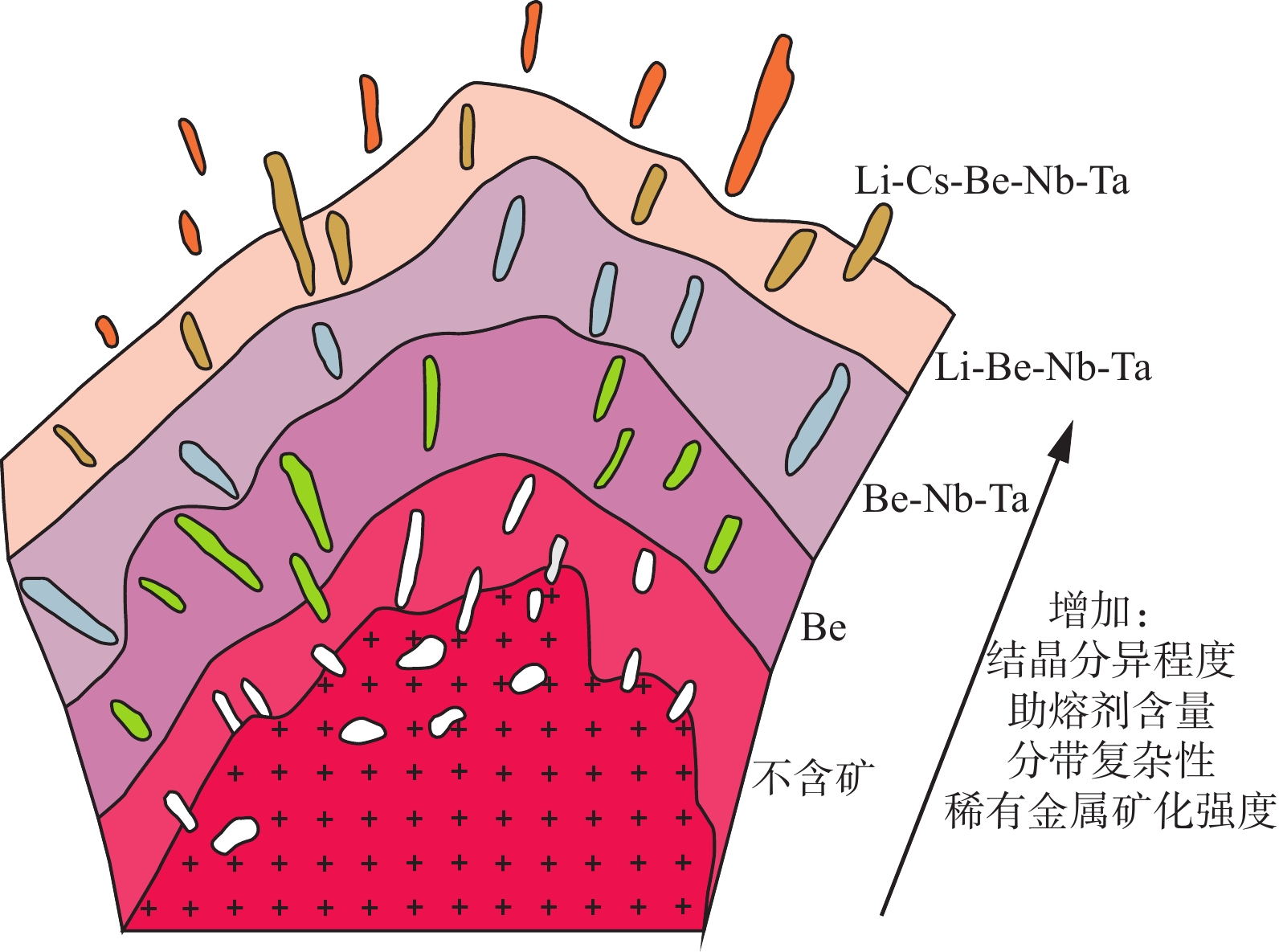
伟晶岩与花岗质岩浆之间的成因联系已被广泛研究证实(Selway et al.,2005)。大多情况下,伟晶岩与花岗岩在时空、物源、岩浆演化上具有相关性,当然,这需要矿物学、地球化学、同位素和地质年代学等方面的证据支持。花岗岩结晶分异模型认为,伟晶岩代表了花岗岩岩浆分离结晶最晚期的产物,分离结晶作用导致参与熔体中的Li、Cs、Ta等不相容元素不断富集,同时B、P、F及H2O等挥发分也增加(London,2008)。挥发分能够降低花岗岩熔体的固相线温度,延长结晶作用的时间,且能降低熔体黏度,提高熔体及其化学元素的扩散速率,最终形成具有粗大晶体的伟晶岩(Simmons et al.,2008)。岩浆结晶分异形成的LCT型伟晶岩通常以花岗岩母岩为中心,分布于10 km半径范围内,并表现出以母体花岗岩为中心的区域分带,表现为从母体花岗岩向外,伟晶岩的结晶分异程度、挥发组分含量、脉体内部分带的复杂性、蚀变程度、稀有金属矿化强度及矿化组合的复杂程度,随着与母体花岗岩的距离增大而增加(图4)。从花岗岩到伟晶岩,稀有金属呈现出无矿化→Be矿化→Be–Nb–Ta矿化→Li–Be–Nb–Ta矿化→Li–Cs–Be–Nb–Ta矿化的区域分带现象(Černý et al.,1991b;Shearer et al.,1992;Selway et al.,2005)。
![]() 图 4 岩浆结晶分异成因的伟晶岩矿化分带模式图(据Černý et al.,1991b修改)Figure 4. Metal zonation of pegmatites derived from mamatic fractionation of a parent granite
图 4 岩浆结晶分异成因的伟晶岩矿化分带模式图(据Černý et al.,1991b修改)Figure 4. Metal zonation of pegmatites derived from mamatic fractionation of a parent granite伟晶岩常产出于高绿片岩相–角闪岩相等变质岩区,与混合片麻岩、混合岩、过铝质花岗岩共生,呈现“变质–变形–岩浆–成矿”四位一体的现象(许志琴等,2019, 2021),而迄今未见侵入于未变质沉积岩中的伟晶岩(Bradley et al.,2017)。另外,由于一些世界级的超大型稀有金属伟晶岩,如澳大利亚的Greenbushes及Wodgina,加拿大的Tanco稀有金属伟晶岩,中国阿尔泰造山带的可可托海3号脉,在空间上未找到有成因联系的花岗岩。研究表明一些稀有金属伟晶岩与周边和区域花岗岩存在形成时代及物源上的解耦(张辉等,2019;Fei et al.,2020;Lv et al.,2021)。从而,一些学者认为存在独立的伟晶岩岩浆,伟晶岩与花岗岩之间可能是兄弟关系,而不是母子关系(Zagorsky,2009),伟晶岩可以直接形成于与区域变质作用相关的地壳深熔作用,即源岩的直接部分熔融。地壳深熔模型提出稀有金属伟晶岩的岩浆形成于在接近花岗岩低共熔的温度条件下,富稀有金属的变沉积岩发生变质脱水和低程度的部分熔融,而形成伟晶岩岩浆(Simmons et al.,2016;张辉等,2019)。
表 2 中国主要花岗伟晶岩型锂矿床及成矿时代统计表Table 2. Formation ages of major pegmatite–type Li deposits in China序号 矿床名称 成矿带 伟晶岩 测试方法 年龄(Ma) 资料来源 1 阿克塔斯 西昆仑 90-1石英钠长锂辉石伟晶岩 锡石LA–ICP–MS U–Pb 218±12 Yan et al.,2018 2 阿克塔斯 西昆仑 90-1石英钠长锂辉石伟晶岩 铌铁矿U–Pb 211.9±2.4 Yan et al.,2018 3 阿克塔斯 西昆仑 含锂辉石伟晶岩 白云母Ar–Ar 185±1 Gao et al.,2020 4 509道班西 西昆仑 含锂辉石伟晶岩 白云母Ar–Ar 197±1 Gao et al.,2020 5 505 西昆仑 18号锂辉石伟晶岩 锡石U–Pb 223±11 李侃等,2019 6 白龙山 西昆仑 含锂辉石伟晶岩 铌钽铁矿U–Pb 208.1±1.5 Wang et al.,2020 7 白龙山 西昆仑 含锂辉石伟晶岩 铌铁矿U–Pb 213.9±0.7 Zhou et al.,2021a 8 白龙山 西昆仑 不含锂辉石伟晶岩 铌铁矿U–Pb 212.3±0.9 Zhou et al.,2021a 9 白龙山 西昆仑 含锂辉石伟晶岩 独居石 U–Pb 207.4±0.6 Yan et al.,2022 10 雪凤岭 西昆仑 含锂辉石伟晶岩 铌钽铁矿U–Pb 208.4±1.7 Yan et al.,2022 11 康西瓦 西昆仑 含绿柱石白云母伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 209±4.4 张泽等,2019 12 肖尔布隆 西昆仑 含锂辉石伟晶岩 铌钽铁矿U–Pb 204.6±2.1 Yan et al.,2022 13 霍什塔什 西昆仑 含锂辉石伟晶岩 铌钽铁矿U–Pb 205.7±2.7 Yan et al.,2022 14 霍什塔什 西昆仑 含锂辉石伟晶岩 独居石 U–Pb 204.2±0.8 Yan et al.,2022 15 木林场 西昆仑 含锂辉石伟晶岩 铌钽铁矿U–Pb 206.4±2.0 Yan et al.,2022 16 吐格曼 阿尔金 电气石钠长石英伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 459.9±3.7 徐兴旺等,2019 17 吐格曼 阿尔金 含稀有金属伟晶岩 铌钽铁矿U–Pb 472±8 Gao et al.,2021 18 吐格曼北 阿尔金 白云母–锡石伟晶岩 锡石LA–ICP–MS U–Pb 468±8.7 李杭等,2020 19 吐格曼北 阿尔金 白云母–钠长石–锂辉石伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 458.7±2.3 李杭等,2020 20 吐格曼北 阿尔金 白云母–钠长石–锂辉石伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 454.7±4.0 李杭等,2020 21 吐格曼北 阿尔金 白云母–钠长石–锂辉石伟晶岩 白云母Ar–Ar 350.2±1.6 李杭等,2020 22 吐格曼北 阿尔金 含铌钽铁矿–白云母–石英伟晶岩 铌钽铁矿U–Pb 464.1±2.7 李杭等,2020 23 茶卡北山 柴北缘 富锂花岗伟晶岩 铌钽铁矿U–Pb 240.6±1.5 Pan et al.,2021 24 茶卡北山 柴北缘 含绿柱石花岗伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 235.9±2.3 王秉璋等,2020 25 茶卡北山 柴北缘 含绿柱石锂辉石花岗伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 217±1.8 王秉璋等,2020 26 锲墨格 柴北缘 绿柱石花岗伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 229.5±1.3 李善平等,2021 27 别也萨麻斯 阿尔泰 锂辉石石英伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 151±1.8 王春龙等,2015 28 卡鲁安 阿尔泰 805号含矿伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 216±2.6 马占龙等,2015 29 卡鲁安 阿尔泰 806号含矿伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 223.7±1.8 马占龙等,2015 30 卡鲁安 阿尔泰 807号含矿伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 221±15 马占龙等,2015 31 卡鲁安 阿尔泰 650号伟晶岩 锆石SIMS U–Pb 205.0±12 刘涛等,2020 32 卡鲁安 阿尔泰 803号含矿伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 224.6±2.3 Zhang et al.,2016 33 库卡拉盖 阿尔泰 650号早期钠长石伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 227.9±2.6 马占龙等,2015 34 库卡拉盖 阿尔泰 650号晚期锂辉石钠
长石锂云母伟晶岩锆石LA–ICP–MS 211.3±2.4 马占龙等,2015 35 可可托海3号脉 阿尔泰 含锂辉石伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 209.4±1.3 闫军武等,2020 36 可可托海3号脉 阿尔泰 伟晶岩 全岩Rb–Sr 218.4±5.8 Zhu et al.,2006 37 可可托海3号脉 阿尔泰 边缘带伟晶岩 辉钼矿Re–Os 208.8±2.4 Liu F et al.,2014 38 可可托海3号脉 阿尔泰 1带伟晶岩 SHRIMP 锆石U–Pb 220±9 Wang et al.,2007 39 可可托海3号脉 阿尔泰 5带伟晶岩 SHRIMP 锆石U–Pb 198±7 Wang et al.,2007 续表2 序号 矿床名称 成矿带 伟晶岩 测试方法 年龄(Ma) 资料来源 40 可可托海3号脉 阿尔泰 7带伟晶岩 SHRIMP 锆石U–Pb 213±6 Wang et al.,2007 41 阿祖拜 阿尔泰 01号含矿伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 191.6±2.0 Zhang et al.,2016 42 佳木开 阿尔泰 09号含矿伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 192.0±2.3 Zhang et al.,2016 43 大喀拉苏 阿尔泰 01号含矿伟晶岩 铌铁矿U–Pb 229.0±1.0 Feng et al.,2020 44 大喀拉苏 阿尔泰 01号含矿伟晶岩 铌铁矿U–Pb 228.1±0.6 Feng et al.,2020 45 加曼哈巴–大喀拉苏 阿尔泰 伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 274~253 Lv et al.,2021 46 科鲁木特112脉 阿尔泰 1号带伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 238.3±2.0 Lv et al.,2012 47 科鲁木特112脉 阿尔泰 2号带伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 233.5±3.7 Lv et al.,2012 48 科鲁木特112脉 阿尔泰 3号带伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 188.3±1.7 Lv et al.,2012 49 科鲁木特112脉 阿尔泰 5号带伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 218.8±1.9 Lv et al.,2012 50 科鲁木特112脉 阿尔泰 6号带伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 210.7±1.6 Lv et al.,2012 51 加曼哈巴 阿尔泰 伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 394.8±4.0 Lv et al.,2018 52 切别林 阿尔泰 伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 402.6±5.5 Lv et al.,2018 53 青河 阿尔泰 塔拉提伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 385.9±3.5 Lv et al.,2018 54 青河 阿尔泰 阿木拉贡伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 358.3±4.6 Lv et al.,2018 55 青河 阿尔泰 阿拉结科伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 368.0±4.0 Lv et al.,2018 56 青河 阿尔泰 铁木勒特伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 333.0±6.0 Lv et al.,2018 57 甲基卡 松潘–甘孜 308号含锂辉石伟晶岩 锡石U–Pb 210.9±4.6 代鸿章等,2018 58 甲基卡 松潘–甘孜 X3号钠长石锂辉石伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 216±2 郝雪峰等,2015 59 甲基卡 松潘–甘孜 X3号钠长石锂辉石伟晶岩 铌钽铁矿U–Pb 214±2 郝雪峰等,2015 60 甲基卡 松潘–甘孜 含矿伟晶岩 锆石SIMS U–Pb 186.7 李贤芳等,2020 61 甲基卡 松潘–甘孜 134号锂辉石伟晶岩 白云母Ar–Ar 195.7±0.1 王登红等,2005 62 甲基卡 松潘–甘孜 104号钠长石伟晶岩 白云母Ar–Ar 198.9±0.4 王登红等,2005 63 甲基卡 松潘–甘孜 308号伟晶岩脉中细晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 217±0.84 Dai et al.,2019 64 甲基卡 松潘–甘孜 308号含锂辉石伟晶岩 锡石U–Pb 211±4.6 Dai et al.,2019 65 甲基卡 松潘–甘孜 133号含锂辉石伟晶岩 锡石U–Pb 198±4.4 Dai et al.,2019 66 李家沟 松潘–甘孜 含锂辉石钠长石伟晶岩 锡石U–Pb 211.4±3.3 许家斌等,2020 67 李家沟 松潘–甘孜 含锂辉石钠长石伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 198±3.4 邓运等,2018 68 李家沟 松潘–甘孜 钠长石伟晶岩 锆石LA–MC–ICP–MS 202.8±4.9 Fei et al.,2020 69 李家沟 松潘–甘孜 钠长石锂辉石伟晶岩 锆石LA–MC–ICP–MS 200.1±4.6 Fei et al.,2020 70 李家沟 松潘–甘孜 钠长石锂辉石伟晶岩 锡石U–Pb 211.4±3.3 Fei et al.,2020 71 李家沟 松潘-甘孜 钠长石锂辉石伟晶岩 铌钽铁矿U–Pb 211.1±1.0 Fei et al.,2020 72 党坝 松潘–甘孜 锂辉石钠长石伟晶岩 锡石U–Pb 208.1±1.9 费光春等,2020 73 党坝 松潘–甘孜 含锂云母锂辉石钠长石伟晶岩 锡石U–Pb 199.3±1.6 费光春等,2020 74 南阳山 东秦岭 363号锂矿化伟晶岩脉 铌钽铁矿U–Pb 387.8±1.6 Zhou et al.,2021b 75 南阳山 东秦岭 364号锂矿化伟晶岩脉 铌钽铁矿U–Pb 383.8±3.3 Zhou et al.,2021b 76 南阳山 东秦岭 366号锂矿化伟晶岩脉 铌钽铁矿U–Pb 422.0±3.2 Zhou et al.,2021b 77 南阳山 东秦岭 366号锂矿化伟晶岩脉 铌钽铁矿U–Pb 397.4±2.2 Zhou et al.,2021b 78 南阳山 东秦岭 703号锂矿化伟晶岩脉 铌钽铁矿U–Pb 409.5±1.5 Zhou et al.,2021b 79 前台 东秦岭 锂矿化伟晶岩脉 铌钽铁矿U–Pb 442.6±8.0 Zhou et al.,2021b 80 前台 东秦岭 锂矿化伟晶岩脉 铌钽铁矿U–Pb 410.8±2.0 Zhou et al.,2021b 2.2 伟晶岩型锂矿床成因机制
针对伟晶岩型稀有金属富集沉淀的机制,前人做了大量的研究,目前主要包括以下几种观点:分离结晶作用(Shearer et al.,1992;Hulsbosch et al.,2014;Wu et al.,2017;Wang et al.,2018)、岩浆液态不混溶作用(Webster et al.,1997;Veksler et al.,2002;李建康等,2007;Zhou et al.,2015)、超临界流体(Thomas et al.,2016,2019;Fan et al.,2020)、组成带状纯化(London,2018)。
分离结晶作用是稀有不相容元素在残余岩浆中高度富集的最重要途径(王汝成等,2019;张辉等,2021),高程度的结晶分异是形成LCT型伟晶岩及稀有金属矿物的有利因素(陈衍景等,2021)。伟晶岩岩浆或熔体富含挥发分B、P、F、Cl、H2O、CO2等,这些挥发分是岩浆形成过程中的助熔剂,是岩浆结晶分异和伟晶岩形成过程中的“传输带”或“搬运夫”。伟晶岩挥发分主要来自源区部分熔融,在熔体/岩浆结晶分异演化过程中富集在残余熔体中,并使稀有金属富集在残余熔体中(陈衍景等,2021)。
另外,在特定的岩浆体系中,岩浆液态分离或熔体-流体的分离(或称之为岩浆液态不混溶)也是稀有金属富集成矿的重要机制。在不混溶形成的富挥发分熔体中,流体较早达到饱和,因此富挥发分的熔体与流体可以长期共存,使成矿元素迁移、富集成矿(Simmons et al.,2008;Thomas et al.,2016)。如中国川西松潘–甘孜成矿带的甲基卡锂矿成矿伟晶岩中的矿物熔融包裹体及流体包裹体共存并具有明显的成矿差异,其锂的富集沉淀机制被解释为流体不混溶作用(李建康等,2007;熊欣等,2019)。
基于包裹体的研究,Thomas等(2012,2016)发现伟晶岩形成中存在熔体A–熔体B–流体三相不混溶作用,并由此提出了伟晶岩形成于超临界流体的观点。这种超临界流体具有极低的密度,极高的扩散性和流动性,超强的元素溶解能力,这些性质使得其携带成矿元素的能力远超水质流体,如Li含量可达28 405×10−6(Thomas et al.,2016)。西昆仑白龙山贫锂和富锂伟晶岩可能分别由贫水富硅酸盐熔体和富水贫硅酸盐熔体(超临界流体)所形成(Fan et al.,2020)。
London(1992,1999,2005,2008,2014,2018)经过一系列的高温高压模拟结晶实验,认为典型伟晶岩的形成过程中,在熔体和结晶前缘之间存在一个富集助熔组分和不相容元素的边界层。助熔组分(B、P、F、H2O)和不相容元素在边界层中的聚集,最后发生边界层熔体的分离结晶作用,导致富挥发分和稀有金属的矿物相饱和结晶(图5),并由此提出了组成带状纯化(CZR–constitutional zone refining)理论(李建康等,2021)。CZR模型强调了富助熔组分的边界层熔体对伟晶岩稀有金属(尤其是Li)富集成矿的重要作用(London,2018)。提出熔体并未达到H2O饱和,结晶作用发生于非平衡的条件下,并能够很好地解释伟晶岩的内部分带现象。此外稀有金属离子及B、P、F在残余富Na、亏损SiO2的熔体中高度富集,揭示了稀有金属矿化出现于晚阶段分异演化程度较高的熔体中(London,1992)。
![]() 图 5 伟晶岩熔体中边界层熔体形成及CZR过程原理图(据London,2018修改)Figure 5. Schematic rendition of the formation of boundary layer liquids and the processes of Compositional Zone Refining (CZR) in pegmatitic liquids
图 5 伟晶岩熔体中边界层熔体形成及CZR过程原理图(据London,2018修改)Figure 5. Schematic rendition of the formation of boundary layer liquids and the processes of Compositional Zone Refining (CZR) in pegmatitic liquids3. 中国西部典型伟晶岩型锂矿带的成矿地质特征及找矿前景
随着关键金属锂的战略作用日益凸显,近几年中央、地方和企业不断加大投入,在中国西部地区大红柳滩及外围、甲基卡、可尔因、阿尔金、柴北缘、青海玉树等地区均取得了重大找矿突破,分析认为这些地区找矿前景巨大。笔者重点选取了中国西部西昆仑、川西松潘–甘孜、阿尔泰3个典型稀有金属成矿带进行详细论述。
3.1 西昆仑稀有金属成矿带
西昆仑地区中生代花岗伟晶岩十分发育,是中国重要的伟晶岩型锂铍成矿带。西昆仑锂铍稀有金属成矿带中的伟晶岩成群成带集中分布,自西北往东南主要分为西段的木吉–布伦口地区、中段的塔什库尔干–麻扎地区、东段的康西瓦–泉水沟地区,构成了一个600 km长的稀有金属成矿带(Yan et al., 2022),主要分布于甜水海及喀喇昆仑地体中,其中以东段的康西瓦–大红柳滩一带最为发育,已发现7 000余条伟晶岩脉(邹天人等,2006)。木吉–布伦口地区主要有卡拉瓦拉锂铍矿点、肖尔布隆锂铍矿点、霍什塔什锂铍矿点、土曼其铍矿点,塔什库尔干–麻扎地区主要有达布达尔铍矿点、三素铍矿点等(图6)(王核等,2021;Yan et al., 2022)。大中型锂铍矿床主要集中分布于康西瓦–大红柳滩一带,自1958年发现阿克塔斯中型锂矿以来,近年该区伟晶岩型锂矿找矿取得重大突破,陆续发现了505中型锂矿、507大型锂矿、俘虏沟南1号大型锂矿、俘虏沟南2号大型锂矿、白龙山超大型锂铷矿床、509道班西大型锂矿、卡拉喀中型锂矿、大红柳滩东中型锂矿、大红柳滩南大型锂铍矿、康西瓦铍矿点、阿克萨依锂矿点(王核等,2017;李侃等,2019;涂其军等,2019)。这些稀有金属矿床(点)均围绕大红柳滩中生代花岗岩基周缘分布,构成了大红柳滩伟晶岩型锂铍矿田。大红柳滩一带累计探获氧化锂资源量约250万t,预测锂资源潜力可达500万t以上,平均品位约1.5%(李文渊等,2021)。
大红柳滩伟晶岩型锂铍矿田大地构造位置上位于康西瓦古特提斯缝合带南侧的巴颜喀拉地块的甜水海地体中,夹持于康西瓦断裂与大红柳滩–郭扎错断裂之间,为古特提斯洋闭合碰撞后的成矿表现(李文渊等,2021)。大红柳滩矿田稀有金属伟晶岩主要呈北西–南东向分布,规模长几十米至上千米,宽几米至百余米,主要分布于三叠系巴颜喀拉山群变质沉积地层中,少量分布于古元古界康西瓦岩群、二叠系黄羊岭群中,花岗岩基中也发育大量的伟晶岩脉,但多不含矿。前人对大红柳滩稀有金属伟晶岩的成矿时代进行了研究,获得了一批高质量的成矿年龄,多集中分布于223~204 Ma(表2)。大红柳滩中生代花岗岩基为复式岩体,东部为黑云母二长花岗岩、含石榴子石(电气石)二长花岗岩,西南部为二云母花岗岩、黑云母花岗岩和花岗闪长岩,岩体的形成时代为220~208.3 Ma(乔耿彪等,2015;魏小鹏等,2017;Ding et al.,2019;Zhang et al.,2019;丁坤等,2020;Wang et al.,2020;Zhou et al.,2021a,2021b;Yan et al.,2022),主要为高钾钙碱性系列S型花岗岩。含锂辉石伟晶岩中白云母40Ar/39Ar 年龄为197~185 Ma,可能代表了伟晶岩热液封闭的时代(Gao et al., 2020)。总体上,伟晶岩稍晚于大红柳滩花岗岩基的形成,均形成于晚三叠世。大红柳滩稀有金属伟晶岩与花岗岩基在形成时间和空间上具有很好的耦合性,笔者认为稀有金属伟晶岩为花岗质岩浆结晶分异的产物。
大红柳滩伟晶岩脉从花岗岩基到远离花岗岩基有明显的分带性(李侃等,2019;李文渊等,2021),由花岗岩基内部至围岩地层,大致表现为电气石伟晶岩→长英质伟晶岩→锂辉石伟晶岩的演变。近岩体地层普遍发生角岩化,热变质作用明显;远离岩体特征变质矿物逐渐由堇青石变为红柱石,反映了温度降低。锂辉石伟晶岩脉一般较远离岩基(体),在约1~4 km范围内产出(Wang et al.,2020;Gao et al.,2020),红柱石化比较发育。
大红柳滩一带三叠纪花岗岩基大面积出露于三十里营房–黄草沟一带,而目前已发现的锂矿床主要分布于岩体南东端围岩–巴颜喀拉山群中,已形成大型矿产资源基地。大红柳滩花岗伟晶岩脉受晚三叠世二云母花岗岩控制,花岗岩岩基边部凸出的岩枝是成矿最有利部位。康西瓦–大红柳滩一带伟晶岩围绕晚三叠世中酸性岩体产出,时间、空间上均与岩体高度耦合,总体上表现出近岩体处脉体密集,远离岩体处则稀疏的特征,据现有资料统计,岩体边部200~1 500 m成矿条件最为有利,已发现的含矿伟晶岩脉大部分位于此范围内。花岗伟晶岩的分布总体与区域构造线方向一致,大多数伟晶岩脉呈北西–南东向展布。伟晶岩脉受岩层节理控制,主要为斜交节理与走向节理。目前,围绕三叠纪岩体周边还有大量伟晶岩脉未查证,区内以Li、Be为主的化探异常广布,多与伟晶岩脉套合,具有较大的找矿前景。已知矿床的外围及深部仍具有较大的找矿潜力。
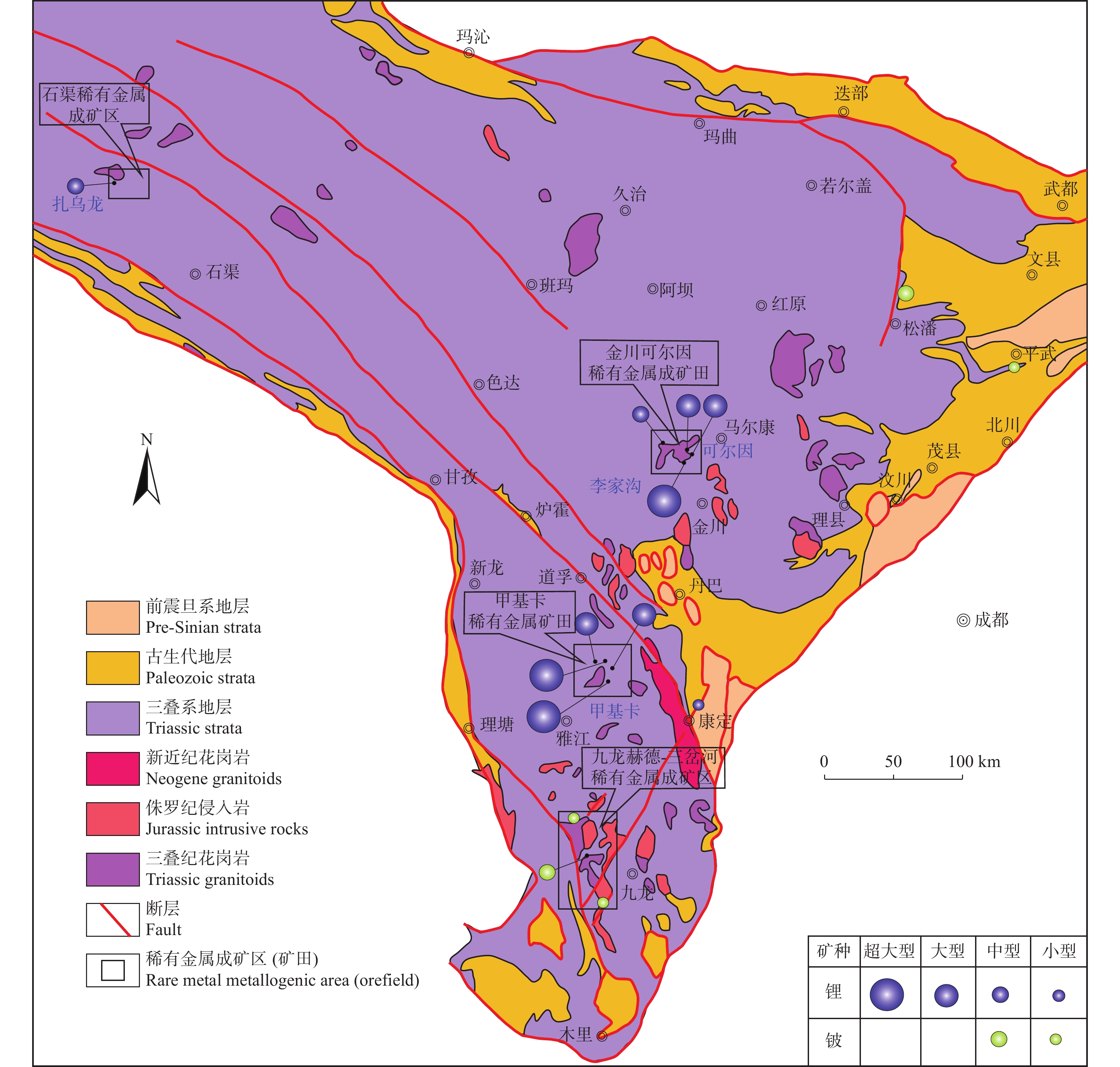
3.2 川西松潘–甘孜稀有金属成矿带
松潘–甘孜造山带内分布有多处超大型和大型伟晶岩型锂矿床,具有规模大、共伴生矿产(Be、Nb、Ta、Rb、Cs、Sn)多、找矿潜力好的特征,是中国重要的稀有金属成矿带(许志琴等,2018,2021;Xu et al.,2020)。川西已发现锂、铍、铌、钽、铷(铯)等矿产地70余处,根据成群成带的产出特征,划分为石渠扎乌龙稀有金属成矿区、康定–雅江稀有金属成矿区(甲基卡矿田)、马尔康–金川稀有金属成矿区(可尔因矿田)以及九龙稀有金属成矿区(图7)(付小方等,2021b)。广泛分布的不同类型的穹隆构造群是松潘–甘孜造山带的重要构造样式,花岗–伟晶岩型锂矿床又大多集结在以花岗岩为核部、三叠纪变质沉积岩为幔部的片麻岩穹隆之中(许志琴等,2018,2021;Xu et al.,2020)。
![]() 图 7 川西松潘–甘孜造山带地质简图及锂铍矿床分布图(据付小方等,2021b)Figure 7. Simplified geological map and distribution of Li–Be deposits of the Songpan–Ganzê orogenic belt, Western Sichuan
图 7 川西松潘–甘孜造山带地质简图及锂铍矿床分布图(据付小方等,2021b)Figure 7. Simplified geological map and distribution of Li–Be deposits of the Songpan–Ganzê orogenic belt, Western Sichuan四川省甘孜州甲基卡花岗伟晶岩型稀有金属矿床是中国目前规模最大的硬岩型稀有金属矿床(刘丽君等,2015;付小方等,2021b),也是世界上最大的伟晶岩型稀有金属矿床之一,目前已经查明的Li2O资源/储量超过200万t。伟晶岩脉多产于花岗岩体顶部内外接触带,其中绝大部分在变质岩内,部分产于内接触带中,伟晶岩的类型(主要根据伟晶岩中造岩矿物划分)发生规律性的变化,呈现出从微斜长石伟晶岩带(Ⅰ)→微斜长石钠长石伟晶岩带(Ⅱ)→钠长石伟晶岩带(Ⅲ)→锂辉石伟晶岩带(Ⅳ)→锂(白) 云母伟晶岩带(Ⅴ)的分带性(付小方等,2015;Li et al.,2016)。甲基卡稀有金属矿(化)脉有378条,以锂为主,次为铍、铌、钽。具有工业价值的矿脉有124条,规模达到大中型以上的矿床(脉)有20余个。代表性矿床(脉)有X03、308、309、134、154、668、638等锂矿脉,其中2012年以来新发现的“新三号脉”(X03)规模最大,单脉氧化锂资源/储量达到89.49万t的超大型规模(付小方等,2021a)。
前人研究表明,与锂矿有关的甲基卡马颈子花岗岩形成年龄为223~206 Ma(郝雪峰等,2015;李贤芳等,2020;Fei et al.,2020),马尔康的可尔因花岗岩形成年龄为226.6~211.9Ma(Zheng et al., 2020)。二者均为二云母花岗岩,并显示高钾钙碱系列和强过铝质的特征,属于S型花岗岩系列(付小方等,2021a;Zheng et al.,2020)。甲基卡稀有金属伟晶岩的成矿时代多集中分布于217~186.7 Ma(表2),可尔因矿田的李家沟伟晶岩型锂矿床锂辉石伟晶岩的形成年龄为211.4~198 Ma(邓运等,2018;许家斌等,2020;Fei et al.,2020),党坝伟晶岩型锂矿床锂辉石伟晶岩的形成年龄为208.1~199.3 Ma(费光春等,2020),总体上,松潘–甘孜锂成矿带的成矿时代为晚三叠世—早侏罗世。
松潘–甘孜稀有金属成矿带与西昆仑大红柳滩均处于青藏高原周缘松潘–甘孜–甜水海地体中,为古特提斯大洋闭合汇聚的产物,在成矿时代、大地构造背景和围岩特征等方面非常相似,有学者将二者统一为西昆仑–松潘–甘孜成矿带(许志琴等,2018,2021;Yan et al.,2022)。甲基卡锂矿累计探明氧化锂资源量188.77万t,外围李家沟及党坝、业隆沟探明氧化锂资源量125.42万t,为中国最大的硬岩型锂矿矿集区,资源潜力巨大。但松潘–甘孜成矿带与西昆仑大红柳滩之间还有大片空白区,未发现稀有金属矿床,尤其是可可西里地区。而青海玉树地区草陇(绿柱石–)锂辉石伟晶岩的发现,进一步说明马尔康‒雅江‒喀喇昆仑巨型锂矿带成矿潜力巨大。该区花岗伟晶岩(矿)脉,成群、成带分布于这些穹窿体周缘的构造裂隙中,隐伏花岗岩株(枝)形成的多中心小穹窿周缘是找矿有利部位(付小方等,2021a)。近年来,除甲基卡的麦基坦(X03)、309、东部烧炭沟等地取得重大找矿勘查成果,氧化锂规模达超大型–大型外,在南部鸭柯柯及外围木绒超大型锂矿的勘探成果均显示了巨大的找矿潜力(付小方等,2021a)。
3.3 阿尔泰稀有金属成矿带
阿尔泰造山带内已发现的伟晶岩脉达10万余条,是中国重要的稀有金属、宝石、工业白云母成矿区(邹天人等,2006;周起凤等,2013)。其稀有金属矿分为花岗伟晶岩型和花岗岩型,以前者为主,分布于哈龙‒青河稀有金属成矿亚带和加曼哈巴‒大喀拉苏稀有金属成矿亚带,共9个矿集区,分别为青河、可可托海、库威–结别特、柯鲁木特–吉德克、卡拉额尔齐斯、大喀拉苏–可可西尔、小喀拉苏–切别林、海流滩–也留曼、加曼哈巴伟晶岩矿集区(图8)(邹天人等,2006;周起凤等,2013;张辉等,2019;Lv et al.,2021)。依据成矿时代,稀有金属成矿作用分为早泥盆世—早石炭世(402~333 Ma)、二叠纪(274~253 Ma)、晚三叠世(238~205 Ma)和侏罗纪(198~151 Ma)4期,其中晚三叠世为主要成矿期(表2)。阿尔泰稀有金属成矿带是一个多旋回成矿作用叠加的复合型成矿带。
![]() 图 8 阿尔泰造山带地质简图(据Lv et al.,2021修改)Figure 8. Sketch geological map of the Altay orogenic belt
图 8 阿尔泰造山带地质简图(据Lv et al.,2021修改)Figure 8. Sketch geological map of the Altay orogenic belt新疆阿尔泰可可托海3号脉伟晶岩型稀有金属矿床是阿尔泰造山带产出的规模最大的伟晶岩脉,以独特的实心礼帽形态、完美的同心环状结构分带和复杂的稀有金属矿化组合闻名于世,是中国最重要的稀有金属矿床之一(邹天人等,2006;秦克章等,2021),并具有“功勋矿脉”的称号(许志琴等,2018)。可可托海3号脉产出于变辉长岩体中,该变辉长岩体形成年龄为409~408 Ma(Wang et al.,2006;Cai et al.,2012)。矿区范围内发育3 种类型花岗岩,分别为黑云母花岗岩、二云母花岗岩和白云母花岗岩,形成年龄为409~388 Ma(Wang et al.,2006;闫军武等,2020),可可托海3号脉形成年龄为220~198 Ma(Zhu et al.,2006;Wang et al.,2007;Liu et al.,2014;闫军武等,2020),与区内岩浆活动时间相差约200 Ma,推断3号伟晶岩及稀有金属矿的形成与矿区岩浆侵入活动没有关系(杨富全等,2018)。另外,马占龙等(2015)通过对卡鲁安矿区伟晶岩和哈龙岩体年代学研究,认为伟晶岩与哈龙岩体之间存在形成时代上的差异(170 Ma以上),预示着它们之间不具成因上的联系,伟晶岩是由陆–陆碰撞体制伸展背景下的加厚地壳物质减压熔融所形成。Lv 等(2021)通过对加曼哈巴–大喀拉苏一带二叠纪稀有金属伟晶岩进行研究,认为其可能为哈巴河群变沉积岩在伸展环境下发生深熔作用的产物。张辉等(2019)认为阿尔泰稀有金属伟晶岩与周边花岗岩存在时代、物源上的解耦,表明伟晶岩的形成与花岗岩无关。由此提出在造山运动过程中加厚的不成熟地壳物质因伸展背景下减压熔融(小比例熔融)形成独立伟晶岩的成因模式。
阿尔泰成矿带除可可托海、卡鲁安、柯鲁木特少数矿床进行过详查和勘探外,多数矿床,特别是小型矿床和矿点,勘查程度低(杨富全等,2020),还具有较大的资源潜力和找矿前景。围绕哈龙花岗岩基分布有柯鲁木特‒吉得克伟晶岩田、阿拉山伟晶岩田、卡鲁安‒阿祖拜伟晶岩田和佳木开‒群库尔伟晶岩田。这4 个伟晶岩田中分布有1 万余条伟晶岩脉,其中代表性的稀有金属伟晶岩矿床,包括卡鲁安Li矿床、库卡拉盖Li矿床、柯鲁木特Li–Be–Nb–Ta矿床、佳木开碧玺矿及群库尔Be–Nb–Ta矿床(杨富全等,2018),构成了一条重要的中生代稀有金属伟晶岩成矿带,具有重要的成矿潜力。
4. 结语
伟晶岩型锂矿是锂资源的主要来源之一,稀有金属花岗伟晶岩可划分为LCT(Li–Cs–Ta)、NYF(Nb–Y–F)及二者混合的LCT+NYF型,其中LCT型伟晶岩富集稀有元素Li、Rb、Cs、Be、Ga、Sn、Ta>Nb及B、P、F等助熔剂,通常与伸展背景下的晚造山和造山后阶段过铝质S型花岗岩具有成因联系。在全球范围内,伟晶岩型锂矿形成时间与碰撞造山引起的超级大陆拼贴时间具有耦合关系,锂矿成矿事件主要发生在超大陆会聚造山作用的中晚期。中国花岗伟晶岩型锂矿空间分布相对集中,主要分布在阿尔泰、西昆仑–喀喇昆仑、川西松潘–甘孜、东天山、东秦岭、阿尔金、柴北缘、江南及藏南喜马拉雅等9个稀有金属成矿带,成矿期以三叠纪为主。花岗质岩浆结晶分异和下地壳物质低程度的部分熔融是伟晶岩两种主要的形成方式。稀有金属伟晶岩的成矿机制主要有分离结晶作用、岩浆不混溶、超临界流体和组成带状纯化。
在推动中国碳中和国家建设战略及全球能源和科技绿色发展的大背景下,锂的战略地位不断提升,是急需解决的卡脖子性的关键金属。近年来,中国西部地区不断取得伟晶岩型锂矿找矿突破,成矿理论认识也不断发展,厘定了与原特提斯洋闭合后碰撞伸展有关的阿尔金锂成矿带,与晚三叠世古特提斯洋碰撞造山–伸展转换有关的西昆仑、松潘–甘孜伟晶岩型锂成矿带,与新特提斯喜马拉雅碰撞后伸展有关的藏南锂多金属成矿带,提出阿尔泰稀有金属成矿带是一个多旋回成矿作用叠加的复合型成矿带。
然而对于锂的物质来源及稀有金属伟晶岩的成岩成矿机制仍不十分清楚,具有较大的争议。不同成矿带的稀有金属伟晶岩是由壳源沉积岩直接部分熔融的产物还是由高分异花岗岩的残余岩浆固结形成?稀有金属在沉积源区、花岗质母岩浆及伟晶岩岩浆中迁移和超常富集的机理是什么?是当前研究的热点和重要方向。伟晶岩多产于片岩–片麻岩或变质砂岩、板岩等变质岩区,并常与过铝质花岗岩共生,伟晶岩的成矿事件多发生在汇聚造山作用晚期,特别是后碰撞伸展环境,构造–岩浆–变质–成矿的耦合关系,值得深入系统的研究,这也是制约锂成矿作用过程和产出规律的关键科学问题。研究锂的富集机制和关键控矿要素,探索深部成矿动力学背景和富集过程,有利于提升特提斯构造域伟晶岩型锂矿成矿理论研究,并会对中国锂这一关键金属的找矿突破提供有力支撑,可以有效地保障国家战略性矿产资源安全。
-
图 1 全球伟晶岩型锂矿床时空分布图(据陈衍景等,2021修改)
Figure 1. The temporal and spatial distribution map of pegmatite–type Li deposits in the world
图 2 花岗岩和伟晶岩型锂矿年龄统计直方图与超大陆事件(据Dittrich et al.,2019;陈衍景等,2021)
Figure 2. Age histograms of pegmatite Li deposits and granites, showing the time of supercontinent events
图 3 中国主要伟晶岩型锂矿床及成矿带分布图(底图据毛景文等,2019)
Figure 3. The sketch map of major pegmatite–type Li deposits and metallogenic belts in China
图 4 岩浆结晶分异成因的伟晶岩矿化分带模式图(据Černý et al.,1991b修改)
Figure 4. Metal zonation of pegmatites derived from mamatic fractionation of a parent granite
图 5 伟晶岩熔体中边界层熔体形成及CZR过程原理图(据London,2018修改)
Figure 5. Schematic rendition of the formation of boundary layer liquids and the processes of Compositional Zone Refining (CZR) in pegmatitic liquids
图 6 西昆仑造山带地质简图及锂铍矿床分布图(据王核等,2021;Yan et al., 2022)
Figure 6. Simplified geological map and distribution of Li–Be deposits of the Western Kunlun orogenic belt
图 7 川西松潘–甘孜造山带地质简图及锂铍矿床分布图(据付小方等,2021b)
Figure 7. Simplified geological map and distribution of Li–Be deposits of the Songpan–Ganzê orogenic belt, Western Sichuan
图 8 阿尔泰造山带地质简图(据Lv et al.,2021修改)
Figure 8. Sketch geological map of the Altay orogenic belt
表 1 花岗伟晶岩的分类及特征表(据Černý et al.,2005)
Table 1 Petrogenetic classification and characteristics of granitic pegmatites
类型 地球化学特征 伟晶岩组成 内部岩相结构分带 相关花岗岩 潜在的母体花岗岩性质 源岩 LCT型 Li、Rb、Cs、Be、
Sn、Ga、Ta>Nb,
(B、P、F)过铝质–次铝质 岩相分带显著 (同造山)–晚造山–(非造山);成分主要是不均匀 过铝质S, I或混合S+I型 未亏损LCT元素的中–上地壳表壳岩石和基底片麻岩 NYF型 Nb>Ta、Ti、Y、
Sc、REE、Zr、
Th、U及F次铝质–准铝质(–亚碱性) 无–弱的岩相分带 (同造山、晚造山、后造山)–主要为非造山;成分准均匀 (过铝质)–次铝质和准铝质A和I型 亏损LCT元素的中–下地壳麻粒岩,新生花岗岩,地幔物质交代的地壳 LCT+NYF
混合型混合的 次铝质–中等过铝质 出现岩相分带 (后造山)–非造山;成分不均匀 次铝质–弱过铝质 混合的岩石源区;受NYF花岗岩浆同化的上地壳 表 2 中国主要花岗伟晶岩型锂矿床及成矿时代统计表
Table 2 Formation ages of major pegmatite–type Li deposits in China
序号 矿床名称 成矿带 伟晶岩 测试方法 年龄(Ma) 资料来源 1 阿克塔斯 西昆仑 90-1石英钠长锂辉石伟晶岩 锡石LA–ICP–MS U–Pb 218±12 Yan et al.,2018 2 阿克塔斯 西昆仑 90-1石英钠长锂辉石伟晶岩 铌铁矿U–Pb 211.9±2.4 Yan et al.,2018 3 阿克塔斯 西昆仑 含锂辉石伟晶岩 白云母Ar–Ar 185±1 Gao et al.,2020 4 509道班西 西昆仑 含锂辉石伟晶岩 白云母Ar–Ar 197±1 Gao et al.,2020 5 505 西昆仑 18号锂辉石伟晶岩 锡石U–Pb 223±11 李侃等,2019 6 白龙山 西昆仑 含锂辉石伟晶岩 铌钽铁矿U–Pb 208.1±1.5 Wang et al.,2020 7 白龙山 西昆仑 含锂辉石伟晶岩 铌铁矿U–Pb 213.9±0.7 Zhou et al.,2021a 8 白龙山 西昆仑 不含锂辉石伟晶岩 铌铁矿U–Pb 212.3±0.9 Zhou et al.,2021a 9 白龙山 西昆仑 含锂辉石伟晶岩 独居石 U–Pb 207.4±0.6 Yan et al.,2022 10 雪凤岭 西昆仑 含锂辉石伟晶岩 铌钽铁矿U–Pb 208.4±1.7 Yan et al.,2022 11 康西瓦 西昆仑 含绿柱石白云母伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 209±4.4 张泽等,2019 12 肖尔布隆 西昆仑 含锂辉石伟晶岩 铌钽铁矿U–Pb 204.6±2.1 Yan et al.,2022 13 霍什塔什 西昆仑 含锂辉石伟晶岩 铌钽铁矿U–Pb 205.7±2.7 Yan et al.,2022 14 霍什塔什 西昆仑 含锂辉石伟晶岩 独居石 U–Pb 204.2±0.8 Yan et al.,2022 15 木林场 西昆仑 含锂辉石伟晶岩 铌钽铁矿U–Pb 206.4±2.0 Yan et al.,2022 16 吐格曼 阿尔金 电气石钠长石英伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 459.9±3.7 徐兴旺等,2019 17 吐格曼 阿尔金 含稀有金属伟晶岩 铌钽铁矿U–Pb 472±8 Gao et al.,2021 18 吐格曼北 阿尔金 白云母–锡石伟晶岩 锡石LA–ICP–MS U–Pb 468±8.7 李杭等,2020 19 吐格曼北 阿尔金 白云母–钠长石–锂辉石伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 458.7±2.3 李杭等,2020 20 吐格曼北 阿尔金 白云母–钠长石–锂辉石伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 454.7±4.0 李杭等,2020 21 吐格曼北 阿尔金 白云母–钠长石–锂辉石伟晶岩 白云母Ar–Ar 350.2±1.6 李杭等,2020 22 吐格曼北 阿尔金 含铌钽铁矿–白云母–石英伟晶岩 铌钽铁矿U–Pb 464.1±2.7 李杭等,2020 23 茶卡北山 柴北缘 富锂花岗伟晶岩 铌钽铁矿U–Pb 240.6±1.5 Pan et al.,2021 24 茶卡北山 柴北缘 含绿柱石花岗伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 235.9±2.3 王秉璋等,2020 25 茶卡北山 柴北缘 含绿柱石锂辉石花岗伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 217±1.8 王秉璋等,2020 26 锲墨格 柴北缘 绿柱石花岗伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 229.5±1.3 李善平等,2021 27 别也萨麻斯 阿尔泰 锂辉石石英伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 151±1.8 王春龙等,2015 28 卡鲁安 阿尔泰 805号含矿伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 216±2.6 马占龙等,2015 29 卡鲁安 阿尔泰 806号含矿伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 223.7±1.8 马占龙等,2015 30 卡鲁安 阿尔泰 807号含矿伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 221±15 马占龙等,2015 31 卡鲁安 阿尔泰 650号伟晶岩 锆石SIMS U–Pb 205.0±12 刘涛等,2020 32 卡鲁安 阿尔泰 803号含矿伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 224.6±2.3 Zhang et al.,2016 33 库卡拉盖 阿尔泰 650号早期钠长石伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 227.9±2.6 马占龙等,2015 34 库卡拉盖 阿尔泰 650号晚期锂辉石钠
长石锂云母伟晶岩锆石LA–ICP–MS 211.3±2.4 马占龙等,2015 35 可可托海3号脉 阿尔泰 含锂辉石伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 209.4±1.3 闫军武等,2020 36 可可托海3号脉 阿尔泰 伟晶岩 全岩Rb–Sr 218.4±5.8 Zhu et al.,2006 37 可可托海3号脉 阿尔泰 边缘带伟晶岩 辉钼矿Re–Os 208.8±2.4 Liu F et al.,2014 38 可可托海3号脉 阿尔泰 1带伟晶岩 SHRIMP 锆石U–Pb 220±9 Wang et al.,2007 39 可可托海3号脉 阿尔泰 5带伟晶岩 SHRIMP 锆石U–Pb 198±7 Wang et al.,2007 续表2 序号 矿床名称 成矿带 伟晶岩 测试方法 年龄(Ma) 资料来源 40 可可托海3号脉 阿尔泰 7带伟晶岩 SHRIMP 锆石U–Pb 213±6 Wang et al.,2007 41 阿祖拜 阿尔泰 01号含矿伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 191.6±2.0 Zhang et al.,2016 42 佳木开 阿尔泰 09号含矿伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 192.0±2.3 Zhang et al.,2016 43 大喀拉苏 阿尔泰 01号含矿伟晶岩 铌铁矿U–Pb 229.0±1.0 Feng et al.,2020 44 大喀拉苏 阿尔泰 01号含矿伟晶岩 铌铁矿U–Pb 228.1±0.6 Feng et al.,2020 45 加曼哈巴–大喀拉苏 阿尔泰 伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 274~253 Lv et al.,2021 46 科鲁木特112脉 阿尔泰 1号带伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 238.3±2.0 Lv et al.,2012 47 科鲁木特112脉 阿尔泰 2号带伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 233.5±3.7 Lv et al.,2012 48 科鲁木特112脉 阿尔泰 3号带伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 188.3±1.7 Lv et al.,2012 49 科鲁木特112脉 阿尔泰 5号带伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 218.8±1.9 Lv et al.,2012 50 科鲁木特112脉 阿尔泰 6号带伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 210.7±1.6 Lv et al.,2012 51 加曼哈巴 阿尔泰 伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 394.8±4.0 Lv et al.,2018 52 切别林 阿尔泰 伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 402.6±5.5 Lv et al.,2018 53 青河 阿尔泰 塔拉提伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 385.9±3.5 Lv et al.,2018 54 青河 阿尔泰 阿木拉贡伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 358.3±4.6 Lv et al.,2018 55 青河 阿尔泰 阿拉结科伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 368.0±4.0 Lv et al.,2018 56 青河 阿尔泰 铁木勒特伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 333.0±6.0 Lv et al.,2018 57 甲基卡 松潘–甘孜 308号含锂辉石伟晶岩 锡石U–Pb 210.9±4.6 代鸿章等,2018 58 甲基卡 松潘–甘孜 X3号钠长石锂辉石伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 216±2 郝雪峰等,2015 59 甲基卡 松潘–甘孜 X3号钠长石锂辉石伟晶岩 铌钽铁矿U–Pb 214±2 郝雪峰等,2015 60 甲基卡 松潘–甘孜 含矿伟晶岩 锆石SIMS U–Pb 186.7 李贤芳等,2020 61 甲基卡 松潘–甘孜 134号锂辉石伟晶岩 白云母Ar–Ar 195.7±0.1 王登红等,2005 62 甲基卡 松潘–甘孜 104号钠长石伟晶岩 白云母Ar–Ar 198.9±0.4 王登红等,2005 63 甲基卡 松潘–甘孜 308号伟晶岩脉中细晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 217±0.84 Dai et al.,2019 64 甲基卡 松潘–甘孜 308号含锂辉石伟晶岩 锡石U–Pb 211±4.6 Dai et al.,2019 65 甲基卡 松潘–甘孜 133号含锂辉石伟晶岩 锡石U–Pb 198±4.4 Dai et al.,2019 66 李家沟 松潘–甘孜 含锂辉石钠长石伟晶岩 锡石U–Pb 211.4±3.3 许家斌等,2020 67 李家沟 松潘–甘孜 含锂辉石钠长石伟晶岩 锆石LA–ICP–MS 198±3.4 邓运等,2018 68 李家沟 松潘–甘孜 钠长石伟晶岩 锆石LA–MC–ICP–MS 202.8±4.9 Fei et al.,2020 69 李家沟 松潘–甘孜 钠长石锂辉石伟晶岩 锆石LA–MC–ICP–MS 200.1±4.6 Fei et al.,2020 70 李家沟 松潘–甘孜 钠长石锂辉石伟晶岩 锡石U–Pb 211.4±3.3 Fei et al.,2020 71 李家沟 松潘-甘孜 钠长石锂辉石伟晶岩 铌钽铁矿U–Pb 211.1±1.0 Fei et al.,2020 72 党坝 松潘–甘孜 锂辉石钠长石伟晶岩 锡石U–Pb 208.1±1.9 费光春等,2020 73 党坝 松潘–甘孜 含锂云母锂辉石钠长石伟晶岩 锡石U–Pb 199.3±1.6 费光春等,2020 74 南阳山 东秦岭 363号锂矿化伟晶岩脉 铌钽铁矿U–Pb 387.8±1.6 Zhou et al.,2021b 75 南阳山 东秦岭 364号锂矿化伟晶岩脉 铌钽铁矿U–Pb 383.8±3.3 Zhou et al.,2021b 76 南阳山 东秦岭 366号锂矿化伟晶岩脉 铌钽铁矿U–Pb 422.0±3.2 Zhou et al.,2021b 77 南阳山 东秦岭 366号锂矿化伟晶岩脉 铌钽铁矿U–Pb 397.4±2.2 Zhou et al.,2021b 78 南阳山 东秦岭 703号锂矿化伟晶岩脉 铌钽铁矿U–Pb 409.5±1.5 Zhou et al.,2021b 79 前台 东秦岭 锂矿化伟晶岩脉 铌钽铁矿U–Pb 442.6±8.0 Zhou et al.,2021b 80 前台 东秦岭 锂矿化伟晶岩脉 铌钽铁矿U–Pb 410.8±2.0 Zhou et al.,2021b -
陈衍景, 薛莅治, 王孝磊, 等. 世界伟晶岩型锂矿床地质研究进展[J]. 地质学报, 2021, 95(10): 2971-2995 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.10.004 CHEN Yanjing, XUE Lizhi, WANG Xiaolei, et al. Progress in geological study of pegmatite-type lithium deposits in the world[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021, 95(10): 2971-2995. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.10.004
陈郑辉, 王登红, 龚羽飞, 等. 新疆哈密镜儿泉伟晶岩型稀有金属矿40Ar/39Ar年龄及其地质意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2006, 25(4): 470-476 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2006.04.011 CHEN Zhenghui, WANG Denghong, Gong Yufei, et al. 40Ar/39Ar isotope dating of muscovite from Jingerquan pegmatite rare metal deposit in Hami, Xinjiang, and its geological significance[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2006, 25(4): 470-476. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7106.2006.04.011
代鸿章, 王登红, 刘丽君, 等. 川西甲基卡308号伟晶岩脉年代学和地球化学特征及其地质意义[J]. 地球科学, 2018, 43(10): 3664-3681 DAI Hongzhang, WANG Denghong, LIU Lijun, et al. Geochronology, geochemistry and their geological significances of No. 308 pegmatite vein in the Jiajika deposit, western Sichuan, China[J]. Earth Science, 2018, 43(10): 3664-3681.
邓运, 费光春, 李剑, 等. 四川李家沟伟晶岩型锂辉石矿床碳氢氧同位素及成矿时代研究[J]. 矿物岩石, 2018, 38(3): 40-47 DENG Yun, FEI Guangchun, LI Jian, et al. Study of C-H-O isotopes and geochronology of the Lijiagou pegmatite spodumene deposit in Sichuan Province[J]. Journal of Mineral Petrology, 2018, 38(3): 40-47.
丁坤, 梁婷, 周义, 等. 西昆仑大红柳滩黑云母二长花岗岩岩石成因: 来自锆石U-Pb年龄及Li-Hf同位素的证据[J]. 西北地质, 2020, 53(1): 24-34 DING Kun, LIANG Ting, ZHOU Yi, et al. Petrogenesis of the Dahongliutan biotite monzogranite in western Kunlun orogen: Evidence from zircon U-Pb age and Li-Hf isotope[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2020, 53(1): 24-34.
费光春, 杨峥, 杨继忆, 等. 四川马尔康党坝花岗伟晶岩型稀有金属矿床成矿时代的限定: 来自LA-MC-ICP-MS锡石 U-Pb定年的证据[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(3): 836-849 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.03.012 FEI Guangchun, YANG Zheng, YANG Jiyi, et al. New precise timing constraint for the Dangba granitic pegmatite type rare- metal deposits, Markam, Sichuan Province: Evidence from cassiterite LA-MC-ICP-MS U-Pb dating[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(3): 836-849. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.03.012
付小方, 袁蔺平, 王登红, 等. 四川甲基卡矿田新三号稀有金属矿脉的成矿特征与勘查模型[J]. 矿床地质, 2015, 34(6): 1172-1186 FU Xiaofang, YUAN Linping, WANG Denghong, et al. Mineralization characteristics and prospecting model of newly discovered X03 rare metal vein in Jiajika orefield, Sichuan[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2015, 34(6): 1172-1186.
付小方, 黄韬, 邹付戈, 等. 甲基卡式锂矿田控矿作用与深部找矿方向[J]. 地质学报, 2021a, 95(3): 791-808 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.03.013 FU Xiaofang, HUANG Tao, ZOU Fuge, et al. Ore-controlling mechanism and deep prospecting direction of Jiajika-like lithium mines[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021a, 95(3): 791-808. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.03.013
付小方, 梁斌, 邹付戈, 等. 川西甲基卡锂等稀有多金属矿田成矿地质特征与成因分析[J]. 地质学报, 2021b, 95(10): 3054-3068 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.10.008 FU Xiaofang, LIANG Bin, ZOU Fuge, et al. Discussion on metallogenic geological characteristics and genesis of rare polymetallic ore fields in western Sichuan[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021b, 95(10): 3054-3068. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.10.008
郝雪峰, 付小方, 梁斌, 等. 川西甲基卡花岗岩和新三号矿脉的形成时代及意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2015, 34(6): 1199-1208 HAO Xuefeng, FU Xiaofang, LIANG Bin, et al. Formation ages of granite and X03 pegmatite vein in Jiajika, western Sichuan and their geological significance[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2015, 34(6): 1199-1208.
李杭, 洪涛, 杨智全, 等. 稀有金属花岗伟晶岩锆石、锡石与铌钽铁矿U-Pb和白云母40Ar/39Ar测年对比研究—以阿尔金中段吐格曼北锂铍矿床为例[J]. 岩石学报, 2020, 36(9): 2869-2892 doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2020.09.16 LI Hang, HONG Tao, YANG Zhiquan, et al. Comparative studying on zircon, cassiterite and coltan U-Pb dating and 40Ar/39Ar dating of muscovite rare-metal granitic pegmatites: A case study of the northern Tugeman lithium-beryllium deposit in the middle of Altyn Tagh[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2020, 36(9): 2869-2892. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2020.09.16
李寄邦, 张辉, 吕正航. 东天山镜儿泉伟晶岩与花岗岩成因关系: 来自锆石U-Pb定年和Hf同位素证据[J]. 地球化学, 2020, 49(4): 385-403 LI Jibang, ZHANG Hui, LÜ Zhenghang. Genetic linkage between pegmatites and granites from Jingerquan, East Tianshan Mountains: Evidence from zircon U-Pb geochronological and Hf isotopic data[J]. Geochimica, 2020, 49(4): 385-403.
李建康, 李鹏, 严清高, 等. 中国花岗伟晶岩的研究历程及发展态势[J]. 地质学报, 2021, 95(10): 2996-3016 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.10.005 LI Jiankang, LI Peng, YAN Qinggao, et al. History of granitic pegmatite research in China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021, 95(10): 2996-3016. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.10.005
李建康, 刘喜方, 王登红. 中国锂矿成矿规律概要[J]. 地质学报, 2014, 88(12): 2269-2283 LI Jiankang, LIU Xifang, WANG Denghong. The Metallogenetic Regularity of Lithium Deposit in China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2014, 88(12): 2269-2283.
李建康, 王登红, 张德会, 等. 川西典型伟晶岩型矿床的形成机制及大陆动力学背景[M]. 北京: 原子能出版社, 2007, 72 – 122 LI Jiankang, WANG Denghong, ZHANG Dehui, et al. Mineralization Mechanism and Continental Geodynamic of Pegmatite Type Deposits in Western Sichuan, China[M]. Beijing: Atomic Energy Press, 2007, 72 – 122.
李侃, 高永宝, 滕家欣, 等. 新疆和田县大红柳滩一带花岗伟晶岩型稀有金属矿成矿地质特征、成矿时代及找矿方向[J]. 西北地质, 2019, 52(4): 206-221 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2019.04.016 LI Kan, GAO Yongbao, TENG Jiaxin, et al. Metallogenic geological characteristics, mineralization age and resource potential of the granite-pegmatite-type rare metal deposits in Dahongliutan area, Hetian County, Xinjiang[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2019, 52(4): 206-221. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6248.2019.04.016
李鹏, 刘翔, 李建康, 等. 湘东北仁里-传梓源矿床5号伟晶岩岩相学、地球化学特征及成矿时代[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(6): 1374-1391 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2019.06.016 LI Peng, LIU Xiang, LI Jiankang, et al. Mineralogical and geochemical characteristics of Renli-Chuanziyuan No. 5 pegmatite, NE Hunan, and its metallogenic epoch[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(6): 1374-1391. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2019.06.016
李善平, 潘彤, 王秉璋, 等. 柴达木盆地北缘锲墨格山含绿柱石花岗伟晶岩特征及构造意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2021, 45(3): 608-619 LI Shanping, PAN Tong, WANG Bingzhang, et al. Characteristics and tectonic significance of beryl-bearing pegmatites in Qiemoge Mountain, northern margin of Qaidam Basin[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2021, 45(3): 608-619.
李文渊, 张照伟, 高永宝, 等.昆仑古特提斯构造转换与镍钴锰锂关键矿产成矿作用研究[J].中国地质, 2022, 49(5): 1385-1407. LI Wenyuan, ZHANG Zhaowei, GAO Yongbao, et al. Tectonic transformation of the Kunlun Paleo-Tethyan orogenic belt and related mineralization of critical mineral resources of nickel, cobalt, manganese and lithium[J]. Geology in China, 2022, 49(5): 1385-1407.
李五福, 李善平, 王秉璋, 等. 青海三江北段草陇(绿柱石-)锂辉石花岗伟晶岩的发现及其Li-Be找矿意义[J/OL]. 大地构造与成矿学. https: //doi. org/10.16539/j. ddgzyckx. 2021.05. 021 LI Wufu, LI Shanping, WANG Bingzhang, et al. Discovery of the (Beryl-bearing) Spodumene Pegmatite in the Caolong Area in the Sanjiang Northern Section of the Qinghai: Implications for Li-Be Mineralization[J/OL]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia.https://doi.org/10.16539/j.ddgzyckx.2021.05.021
李贤芳, 田世洪, 王登红, 等. 川西甲基卡锂矿床花岗岩与伟晶岩成因关系: U-Pb定年、Hf-O同位素和地球化学证据[J]. 矿床地质, 2020, 39(2): 273-304 LI XianFang, TIAN Shihong, WANG Denghong, et al. Genetic relationship between pegmatite and granite in Jiajika lithium deposit in western Sichuan: Evidence from zircon U-Pb dating, Hf-O isotope and geochemistry [J]. Mineral Deposits, 2020, 39(2): 273-304.
刘丽君, 付小方, 王登红, 等. 甲基卡式稀有金属矿床的地质特征与成矿规律[J]. 矿床地质, 2015, 34(6): 1187-1198 LIU Lijun, FU Xiaofang, WANG Denghong, et al. Geological characteristics and metallogeny of Jiajika-style rare metal deposits[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2015, 34(6): 1187-1198.
刘涛, 田世洪, 王登红, 等. 新疆卡鲁安硬岩型锂矿床花岗岩与伟晶岩成因关系: 锆石U-Pb定年、Hf-O同位素和全岩地球化学证据[J]. 地质学报, 2020, 94(11): 3293-3320 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.11.009 LIU Tao, TIAN Shihong, WANG Denghong, et al. Genetic relationship between granite and pegmatite in Kalu'an hard-rock-type lithium deposit in Xinjiang: results from zircon U-Pb dating, Hf-O isotopes and whole-rock geochemistry[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2020, 94(11): 3293-3320. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2020.11.009
刘翔, 周芳春, 李鹏, 等. 湖南仁里稀有金属矿田地质特征、成矿时代及其找矿意义[J]. 矿床地质, 2019, 38(4): 771-791 doi: 10.16111/j.0258-7106.2019.04.007 LIU Xiang, ZHOU Fangchun, LI Peng, et al. Geological characteristics and metallogenic age of Renli rare metal orefield in Hunan and its prospecting significance[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2019, 38(4): 771-791. doi: 10.16111/j.0258-7106.2019.04.007
马占龙, 张辉, 唐勇, 等. 新疆卡鲁安矿区伟晶岩锆石U-Pb定年、铪同位素组成及其与哈龙花岗岩成因关系研究[J]. 地球化学, 2015, 44(1): 9-26 doi: 10.19700/j.0379-1726.2015.01.002 MA Zhanlong, ZHANG Hui, TANG Yong, et al. Zircon U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotopes of pegmatites from the Kalu'an mining area in the Altay, Xinjiang and their genetic relationship with the Halong granite[J]. Geochimica, 2015, 44(1): 9-26. doi: 10.19700/j.0379-1726.2015.01.002
毛景文, 袁顺达, 谢桂青, 等. 21世纪以来中国关键金属矿产找矿勘查与研究新进展[J]. 矿床地质, 2019, 38(5): 935-969 doi: 10.16111/j.0258-7106.2019.05.001 MAO Jingwen, YUAN Shunda, XIE Guiqing, et al. New advances on metallogenic studies and exploration on critical minerals of China in 21st century[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2019, 38(5): 935-969. doi: 10.16111/j.0258-7106.2019.05.001
乔耿彪, 张汉德, 伍跃中, 等. 西昆仑大红柳滩岩体地质和地球化学特征及对岩石成因的制约[J]. 地质学报, 2015, 89(7): 1180-1194 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2015.07.003 QIAO Gengbiao, ZHANG Hande, WU Yuezhong, et al. Petrogenesis of the Dahongliutan monzogranite in Western Kunlun: constraints from SHRIMP zircon U-Pb geochronology and geochemical characteristics[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2015, 89(7): 1180-1194. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2015.07.003
秦克章, 周起凤, 唐冬梅, 等. 阿尔泰可可托海3号脉花岗伟晶岩侵位机制、熔-流体演化、稀有金属富集机理及待解之谜[J]. 地质学报, 2021, 95(10): 3039-3053 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.10.007 QIN Kezhang, ZHOU Qifeng, TANG Dongmei, et al. The emplacement mechnism, melt-fluid evolution, rare-element metallogenesis and puzzles of the Koktokay No. 3 pegmatitic rare element deposit, Altai[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021, 95(10): 3039-3053. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.10.007
涂其军, 韩琼, 李平, 等. 西昆仑大红柳滩一带锂辉石矿基本特征和勘查新进展[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(11): 2862-2873 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2019.11.011 TU Qijun, HAN Qiong, LI Ping, et al. Basic characteristics and exploitation progress of the spodumene ore deposit in the Dahongliutan area, West Kunlun[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(11): 2862-2873. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2019.11.011
王秉璋, 韩杰, 谢祥镭, 等. 青藏高原东北缘茶卡北山印支期(含绿柱石)锂辉石伟晶岩脉群的发现及Li-Be成矿意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2020, 44(1): 69-79 WANG Bingzhang, HAN Jie, XIE Xianglei, et al. Discovery of the indosinian (Beryl-bearing) spodumene pegmatitic dike swarm in the Chakabeishan area in the northeastern margin of the Tibetan plateau: implications for Li-Be mineralization[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2020, 44(1): 69-79.
王春龙, 秦克章, 唐冬梅, 等. 阿尔泰阿斯喀尔特Be-Nb-Mo矿床年代学、锆石Hf同位素研究及其意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2015, 31(8): 2337-2352 WANG Chunlong, QIN Kezhang, TANG Dongmei, et al. Geochronology and Hf isotope of zircon for the Arskartor Be-Nb-Mo deposit in Altay and its geological implications[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2015, 31(8): 2337-2352.
王登红. 关键矿产的研究意义、矿种厘定、资源属性、找矿进展、存在问题及主攻方向[J]. 地质学报, 2019, 93(6): 1189-1209 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2019.06.003 WANG Denghong. Study on critical mineral resources: significance of research, determination of types, attributes of resources, progress of prospecting, problems of utilization, and direction of exploitation[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2019, 93(6): 1189-1209. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2019.06.003
王登红, 李建康, 付小方. 四川甲基卡伟晶岩型稀有金属矿床的成矿时代及其意义[J]. 地球化学, 2005, 34(6): 541-547 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2005.06.001 WANG Denghong, LI Jiankang, FU Xiaofang. 40Ar/39Ar dating for the Jiajika pegmatite-type rare metal deposit in western Sichuan and its significance[J]. Geochemica, 2005, 34(6): 541-547. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0379-1726.2005.06.001
王核, 李沛, 马华东, 等. 新疆和田县白龙山超大型伟晶岩型锂铷多金属矿床的发现及其意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2017, 41(6): 1053-1062 WANG He, LI Pei, MA Huadong, et al. Discovery of the Bailongshan superlarge lithium-rubidium deposit in Karakorum, Hetian, Xinjiang, and its prospecting implication[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2017, 41(6): 1053-1062.
王核, 徐义刚, 闫庆贺, 等. 新疆白龙山伟晶岩型锂矿床研究进展[J]. 地质学报, 2021, 95(10): 3085-3098 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.10.010 WANG He, XU Yigang, YAN Qinghe, et al. Research progress on Bailongshan pegmatite type lithium deposit, Xinjiang[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021, 95(10): 3085-3098. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.10.010
王汝成, 谢磊, 诸泽颖, 等. 云母: 花岗岩-伟晶岩稀有金属成矿作用的重要标志矿物[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(1): 69-75 doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.01.04 WANG Rucheng, XIE Lei, ZHU Zeying, et al. Micas: important indicators of granite-pegmatite-related rare-metal mineralization[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2019, 35(1): 69-75. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.01.04
王瑞江, 王登红, 李建康, 等. 稀有稀土稀散矿产资源及其开发利用[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2015, 1−429 WANG Ruijiang, WANG Denghong, LI Jiankang, et al. Mineral Resources and Mineral Development of Rare Earth, Rare Metal and Rare-Scattered Elements Mineral Resources[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2015, 1-429.
魏小鹏, 王核, 胡军, 等. 西昆仑大红柳滩二云母花岗岩地球化学和地质年代学研究及其地质[J]. 地球化学, 2017, 46(1): 66-80 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2017.01.006 WEI Xiaopeng, WANG He, HU Jun, et al. Geochemistry and geochronology of the Dahongliutan two-mica granite pluton in western Kunlun orogen: Geotectonic implications[J]. Geochimica, 2017, 46(1): 66-80. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0379-1726.2017.01.006
熊欣, 李建康, 王登红, 等. 川西甲基卡花岗伟晶岩型锂矿床中熔体、流体包裹体固相物质研究[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 2019, 38(2): 241-253 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2019.02.008 XIONG Xin, LI Jiankang, WANG Denghong, et al. A study of solid minerals in melt inclusions and fluid inclusions from the Jiajika pegmatite-type lithium deposit[J]. Acta Petrologica et Mineralogica, 2019, 38(2): 241-253. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6524.2019.02.008
许家斌, 费光春, 覃立业, 等. 四川可尔因矿田李家沟伟晶岩型稀有金属矿床锡石LA-MC-ICP-MS U-Pb定年及地质意义[J]. 地质与勘探, 2020, 56(2): 346-358 XU Jiabin, FEI Guangchun, QIN Liye, et al. LA-MC-ICP-MS U-Pb dating of cassiterite from the Lijiagou pegmatite-type rare-metal deposit in the Ke'eryin orefield, Sichuan Province and its geological implication[J]. Geology and Exploration, 2020, 56(2): 346-358.
徐兴旺, 李杭, 石福品, 等. 阿尔金中段吐格曼地区花岗伟晶岩型稀有金属成矿特征与找矿预测[J]. 岩石学报, 2019, 35(11): 3303-3316 doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.11.03 XU Xingwang, LI Hang, SHI Fupin, et al. Metallogenic characteristics and prospecting of granitic pegmatite-type rare metal deposits in the Tugeman area, middle part of Altyn Tagh[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2019, 35(11): 3303-3316. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.11.03
许志琴, 付小方, 赵中宝, 等. 片麻岩穹隆与伟晶岩型锂矿的成矿规律探讨[J]. 地球科学, 2019, 44(5): 1452-1463 XU Zhiqin, FU Xiaofang, ZHAO Zhongbao, et al. Discussion on relationships of gneiss dome and metallogenic regularity of pegmatite-type lithium deposits[J]. Earth Science, 2019, 44(5): 1452-1463.
许志琴, 王汝成, 赵中宝, 等. 试论中国大陆“硬岩型”大型锂矿带的构造背景[J]. 地质学报, 2018, 92(6): 1091-1106 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2018.06.001 XU Zhiqin, WANG Rucheng, ZHAO Zhongbao, et al. On the Structural Backgrounds of the Large-scale "Hard-rock Type" Lithium Ore Belts in China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2018, 92(6): 1091-1106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2018.06.001
许志琴, 朱文斌, 郑碧海, 等. 新能源锂矿战略与大陆动力学研究——纪念南京大学地球科学与工程学院100周年华诞[J]. 地质学报, 2021, 95(10): 2937-2954 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.10.002 XU Zhiqin, ZHU Wenbin, ZHENG Bihai, et al. New energy strategy for lithium resource and the continental dynamics research—celebrating the centenary of the School of Earth Sciences and Engineering, Nanjing University[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021, 95(10): 2937-2954. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.10.002
闫军武, 刘锋, 申颖, 等. 新疆可可托海伟晶岩田岩浆活动时限与伟晶岩形成[J]. 地球学报, 2020, 41(5): 663-674 doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2020.072701 YAN Junwu, LIU Feng, SHEN Ying, et al. Constraints on timing of magmatic activity and formation of pegmatite in the Koktokay pegmatite field, Xinjiang[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2020, 41(5): 663-674. doi: 10.3975/cagsb.2020.072701
杨富全, 张志欣, 刘国仁, 等. 新疆中亚造山带三叠纪矿床地质特征、时空分布及找矿方向[J]. 矿床地质, 2020, 39(2): 197-214 doi: 10.16111/j.0258-7106.2020.02.001 YANG Fuquan, ZHANG Zhixin, LIU Guoren, et al. A review of geological characteristics and time-space distribution as well as prospecting direction of Triassic deposits in Central Asian Orogenic Belt, Xinjiang[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2020, 39(2): 197-214. doi: 10.16111/j.0258-7106.2020.02.001
杨富全, 张忠利, 王蕊, 等. 新疆阿尔泰稀有金属矿地质特征及成矿作用[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 2018, 42(6): 1010-1026 doi: 10.16539/j.ddgzyckx.2018.06.006 YANG Fuquan, ZHANG Zhongli, WANG Rui, et al. Geological characteristics and metallogenesis of rare metal deposits in Altay, Xinjiang[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 2018, 42(6): 1010-1026. doi: 10.16539/j.ddgzyckx.2018.06.006
翟明国, 胡波. 矿产资源国家安全、国际争夺与国家战略之思考[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 2021, 43(1): 1-11 doi: 10.19814/j.jese.2020.10018 ZHAI Mingguo, HU Bo. Thinking to state security, international competition, and national strategy of mineral resources[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2021, 43(1): 1-11. doi: 10.19814/j.jese.2020.10018
翟明国, 吴福元, 胡瑞忠, 等. 战略性关键金属矿产资源: 现状与问题[J]. 中国科学基金, 2019, 33(2): 106-111 ZHAI Mingguo, WU Fuyuan, HU Ruizhong, et al. Critical metal mineral resources: current research status and scientific issues[J]. Science Foundation in China, 2019, 33(2): 106-111.
张辉, 吕正航, 唐勇. 新疆阿尔泰造山带中伟晶岩型稀有金属矿床成矿规律、找矿模型及其找矿方向[J]. 矿床地质, 2019, 38(4): 792-814 doi: 10.16111/j.0258-7106.2019.04.008 ZHANG Hui, LV Zhenghang, TANG Yong. Metallogeny and prospecting model as well as prospecting direction of pegmatite-type rare metal ore deposits in Altay orogenic belt, Xinjiang[J]. Mineral Deposits, 2019, 38(4): 792-814. doi: 10.16111/j.0258-7106.2019.04.008
张辉, 吕正航, 唐勇. LCT型伟晶岩及其锂矿床成因概述[J]. 地质学报, 2021, 95(10): 2955-2970 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.10.003 ZHANG Hui, LV Zhenghang, TANG Yong. A review of LCT pegmatite and its lithium ore genesis[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2021, 95(10): 2955-2970. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2021.10.003
张泽, 梁婷, 凤永刚, 等. 新疆西昆仑造山带康西瓦含绿柱石白云母伟晶岩的地质特征与年代学研究[J]. 西北地质, 2019, 52(1): 75-88 doi: 10.19751/j.cnki.61-1149/p.2019.01.007 ZHANG Ze, LIANG Ting, FENG Yonggang, et al. Geologic feature and chronology study of Kangxiwa beryl-bearing muscovite pegmatite in West Kunlun orogenic belt, Xinjiang[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2019, 52(1): 75-88. doi: 10.19751/j.cnki.61-1149/p.2019.01.007
赵俊兴, 何畅通, 秦克章, 等. 喜马拉雅琼嘉岗超大型伟晶岩锂矿的形成时代、源区特征及分异特征[J]. 岩石学报, 2021, 37(11): 3325-3347 doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2021.11.06 ZHAO Junxing, HE Changtong, QIN Kezhang, et al. Geochronology, source features and the characteristics of the fractional crystallization in pegmatite at the Qiongjiagang giant pegmatite-type lithium deposit, Himalaya, Tibet[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2021, 37(11): 3325-3347. doi: 10.18654/1000-0569/2021.11.06
周起凤, 秦克章, 唐冬梅, 等. 阿尔泰可可托海3号脉伟晶岩型稀有金属矿床云母和长石的矿物学研究及意义[J]. 岩石学报, 2013, 29(9): 3004-3022 ZHOU Qifeng, QIN Kezhang, TANG Dongmei, et al. Mineralogy and significance of micas and feldspars from the Koktokay No. 3 pegmatitic rare- element deposit, Altai[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2013, 29(9): 3004-3022.
邹天人, 李庆昌. 中国新疆稀有及稀土金属矿床[M]. 北京: 地质出版社, 2006, 1 − 284 ZOU Tianren, LI Qingchang. Rare and Rare Earth Metallic Deposits in Xinjiang, China[M]. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2006, 1 − 284.
Bradley D C, McCauley A D, Stillings L L. Mineral-deposit model for lithium-cesium-tantalum pegmatite. Scientific Investigations Report (No. 2010-5070-O). New York: US Geological Survey, 2017, https: //doi. org. /10.3133/sir20105070.
Cai K S, Sun M, Yuan C, et al. Keketuohai mafic-ultramafic complex in the Chinese Altai, NW China: Petrogenesis and geodynamic significance[J]. Chemical Geology, 2012, 294-295: 26-41. doi: 10.1016/j.chemgeo.2011.11.031
Černý P, Ercit T S. The classification of granitic pegmatites revisited[J]. The Canadian Mineralogist, 2005, 43: 2005-2026. doi: 10.2113/gscanmin.43.6.2005
Černý P, London D, Novak M. Granitic pegmatites as reflections of their sources[J]. Elements, 2012, 8: 257-261. doi: 10.2113/gselements.8.4.257
Černý P. Geochemical and petrogenetic features of mineralization in rare-element granitic pegmatites in the light of current research[J]. Applied Geochemistry, 1992, 7: 393-416.
Černý P. Rare-element granite pegmatites. Part I: anatomy and internal evolution of pegmatite deposits[J]. Geoscience Canada, 1991a, 18: 49-67.
Černý P. Rare-element granite pegmatites. Part II: regional to global environments and petrogenesis[J]. Geoscience Canada, 1991b, 18: 68-81.
Dai H Z, Wang D H, Liu L J, et al. Geochronology and geochemistry of Li(Be)-bearing granitic pegmatites from the Jiajika superlarge Li-polymetallic deposit in Western Sichuan, China[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 2019, 30(4): 707-727. doi: 10.1007/s12583-019-1011-9
Dittrich T, Seifert T, Schulz B, et al. Archean Rare-Metal Pegmatites in Zimbabwe and Western Australia: Geology and Metallogeny of Pollucite Mineralisations[M]. Switzerland: Springer, 2019, 1 − 125.
Ding K, Liang T, Yang X Q, et al. Geochronology, petrogenesis and tectonic significance of Dahongliutan pluton in Western Kunlun orogenic belt, NW China[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2019, 26: 3420-3435. doi: 10.1007/s11771-019-4264-7
Fan J J, Tang G, Wei G J, et al. Lithium isotope fractionation during fluid exsolution: Implications for Li mineralization of the Bailongshan pegmatites in the West Kunlun, NW Tibet[J]. Lithos, 2020, 352-353: 105236. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2019.105236
Fei G C, Menuge J F, Li Y Q, et al. Petrogenesis of the Lijiagou spodumene pegmatites in Songpan-Garze Fold Belt, West Sichuan, China: Evidence from geochemistry, zircon, cassiterite and coltan U-Pb geochronology and Hf isotopic compositions[J]. Lithos, 2020, 364-365: 105555.
Feng Y G, Liang T, Linnen R, et al. LA-ICP-MS dating of high‑uranium columbite from no. 1 pegmatite at Dakalasu, the Chinese Altay orogen: Assessing effect of metamictization on age concordance[J]. Lithos, 2020, 362-363: 105461. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2020.105461
Gao Y B, Bagas L, Li K, et al. Newly discovered Triassic lithium deposits in the Dahongliutan area, Northwest China: A case study for the detection of lithium-bearing pegmatite deposits in rugged terrains using remote-sensing data and images[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2020, 8: 591966. doi: 10.3389/feart.2020.591966
Gao Y B, Zhao X M, Bagas L, et al. Newly discovered Ordovician Li-Be deposits at Tugeman in the Altyn-Tagh Orogen, NW China[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2021, 139: 104515. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2021.104515
Hulsbosch N, Hertogen J, Dewaele S, et al. Alkali metal and rare earth element evolution of rock-forming minerals from the Gatumba area pegmatites (Rwanda): quantitative assessment of crystal-melt fractionation in the regional zonation of pegmatite groups[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 2014, 132: 349-374. doi: 10.1016/j.gca.2014.02.006
Kesler S E, Gruber P W, Medina P A, et al. Global lithium resources: Relative importance of pegmatite, brine and other deposits[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2012, 48: 55-69. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2012.05.006
Li J K, Chou I M. An occurrence of metastable cristobalite in spodumene-hosted crystal-rich inclusions from Jiajika pegmatite deposit, China[J]. Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 2016, 171: 29-36. doi: 10.1016/j.gexplo.2015.10.012
Liu C, Wang R C, Wu F Y, et al. Spodumene pegmatites from the Pusila pluton in the higher Himalaya, South Tibet: Lithium mineralization in a highly fractionated leucogranite batholith[J]. Lithos, 2020, 358-359: 105421. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2020.105421
Liu F, Zhang Z X, Li Q, et al. New precise timing constraint for the Keketuohai No. 3 pegmatite in Xinjiang, China, and identification of its parental pluton[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2014, 56: 209-219. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2013.08.020
London D, Evensen J M. Beryllium in silicic magmas and the origin of beryl-bearing pegmatites[J]. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2002, 50(1): 445-486. doi: 10.2138/rmg.2002.50.11
London D, Morgan VI G B. Experimental crystallization of the macusani obsidian, with applications to lithium-rich granitic pegmatites[J]. Journal of Petrology, 2017, 58(5): 1005-1030.
London D. A petrologic assessment of internal zonation in granitic pegmatites[J]. Lithos, 2014, 184-187: 74-104. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2013.10.025
London D. Granitic pegmatites: an assessment of current concepts and directions for the future[J]. Lithos, 2005, 80: 281-303. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2004.02.009
London D. Melt boundary layers and the growth of pegmatitic textures[J]. The Canadian Mineralogist, 1999, 37: 826-827.
London D. Ore-forming processes within granitic pegmatites[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2018, 101: 349-383.
London D. Pegmatites[M]. Canadian Mineralogist Special Publication, 2008, 10: 1 − 368.
London D. The application of experimental petrology to the genesis and crystallization of granitic pegmatites[J]. The Canadian Mineralogist, 1992, 30: 499-540.
London D. The magmatic-hydrothermal transition in the Tanco rare-element pegmatite: evidence from fluid inclusions and phase equilibrium experiments[J]. American Mineralogist, 1986, 71: 376-395.
Lv Z H, Zhang H, Tang Y. Anatexis origin of rare metal/earth pegmatites: Evidences from the Permian pegmatites in the Chinese Altai[J]. Lithos, 2021, 380-381: 105865. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2020.105865
Lv Z H, Zhang H, Tang Y, et al. Petrogenesis and magmatic–hydrothermal evolution time limitation of Kelumute No. 112 pegmatite in Altay, Northwestern China: Evidence from zircon U-Pb and Hf isotopes[J]. Lithos, 2012, 154: 374-391.
Lv Z H, Zhang H, Tang Y, et al. Petrogenesis of syn-orogenic rare metal pegmatites in the Chinese Altai: Evidences from geology, mineralogy, zircon U-Pb age and Hf isotope[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2018, 95: 161-181.
Martin R F, De Vito C. The patterns of enrichment in felsic pegmatites ultimately depend on tectonic setting[J]. The Canadian Mineralogist, 2005, 43: 2027-2048.
Pan T, Ding Q F, Zhou X, et al. Columbite-tantalite group mineral U-Pb geochronology of Chaqiabeishan Li-rich granitic pegmatites in the Quanji Massif, NW China: Implications for the genesis and emplacement ages of pegmatites[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 2021, 8: 606951. doi: 10.3389/feart.2020.606951
Selway J B, Breaks F W, Tindle A G. A review of rare-element (Li-Cs-Ta) pegmatite exploration techniques for the Superior Province, Canada, and large worldwide tantalum deposits[J]. Exploration and Mining Geology, 2005, 14: 1-30. doi: 10.2113/gsemg.14.1-4.1
Shaw R A, Goodenough K M, Roberts N M W, et al. Petrogenesis of rare-metal pegmatites in high-grade metamorphic terranes: A case study from the Lewisian Gneiss Complex of north-west Scotland[J]. Precambrian Research, 2016, 281: 338-362. doi: 10.1016/j.precamres.2016.06.008
Shearer C K, Papike J J, Jolliff B L. Petrogenetic links among granites and pegmatites in the Harney Peak rare-element granite-pegmatite system, Black Hills, South Dakota[J]. The Canadian Mineralogist, 1992, 30: 785-809.
Simmons W B, Webber K L. Pegmatite genesis: State of the art[J]. European Journal of Mineralogy, 2008, 20(4): 421-438. doi: 10.1127/0935-1221/2008/0020-1833
Simmons W, Falster A, Webber K, et al. Bulk composition of the Mt. Mica pegmatite, Maine, USA: implications for the origin of an LCT type pegmatite by anatexis[J]. The Canadian Mineralogist, 2016, 54: 1053-1070. doi: 10.3749/canmin.1600017
Thomas R, Davidson P, Appel K. The enhanced element enrichment in the supercritical states of granite-pegmatite systems[J]. Acta Geochimica, 2019, 38(3): 335-349. doi: 10.1007/s11631-019-00319-z
Thomas R, Davidson P, Beurlen H. The competing models for the origin and internal evolution of granitic pegmatites in the light of melt and fluid inclusion research[J]. Mineralogy and Petrology, 2012, 106: 55-73.
Thomas R, Davidson P. Revisiting complete miscibility between silicate melts and hydrous fluids, and the extreme enrichment of some elements in the supercritical state—Consequences for the formation of pegmatites and ore deposits[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2016, 72: 1088-1101. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2015.10.004
Veksler I V, Thomas R, Schimdt C. Experimental evidence of three coexisting immiscible fluids in synthetic granitic pegmatite[J]. American Mineralogist, 2002, 87: 775-779. doi: 10.2138/am-2002-5-621
Wang H, Gao H, Zhang X Y, et al. Geology and geochronology of the super-large Bailongshan Li–Rb–(Be) rare-metal pegmatite deposit, West Kunlun orogenic belt, NW China[J]. Lithos, 2020, 360-361: 105449. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2020.105449
Wang R C, Zhou M F. Granites: origin and associated mineralization[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2018, 61: 1932-1933.
Wang T, Hong D W, Jahn B M, et al. Timing, petrogenesis, and setting of Paleozoic synorogenic intrusions from the Altai Mountains, Northwest China: Implications for the tectonic evolution of an accretionary orogen[J]. The Journal of Geology, 2006, 114(6): 735-751. doi: 10.1086/507617
Wang T, Tong Y, Jahn B M, et al. SHRIMP U–Pb Zircon geochronology of the Altai No. 3 Pegmatite, NW China, and its implications for the origin and tectonic setting of the pegmatite [J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2007, 32: 325-336. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2006.10.001
Webster J D, Thomas R, Rhede D. Melt inclusions in quartz from an evolved peraluminous pegmatite: geochemical evidence for strong tin enrichment in fluorine-rich and phosphorus-rich residual liquids[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1997, 61(13): 2589-2604. doi: 10.1016/S0016-7037(97)00123-3
Wu F Y, Liu X C, Ji W Q, et al. Highly fractionated granites: recognition and research[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2017, 60: 1201-1219. doi: 10.1007/s11430-016-5139-1
Xu Z Q, Fu X F, Wang R C, et al. Generation of lithium-bearing pegmatite deposits within the Songpan-Ganze orogenic belt, East Tibet[J]. Lithos, 2020, 354-355: 105281. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2019.105281
Yan Q H, Qiu Z W, Wang H, et al. Age of the Dahongliutan rare metal pegmatite deposit, West Kunlun, Xinjiang (NW China): constraints from LA-ICP-MS U-Pb dating of columbite-(Fe) and cassiterite[J]. Ore Geology Reviews, 2018, 100: 561-573. doi: 10.1016/j.oregeorev.2016.11.010
Yan Q H, Wang H, Chi G X, et al. Recognition of a 600-km-long Late Triassic rare-metal (Li–Rb–Be–Nb–Ta) pegmatite belt in the Western Kunlun orogenic belt[J]. Economic Geology, 2022, 117(1): 213-236. doi: 10.5382/econgeo.4858
Yuan F, Liu J J, Carranza E J M, et al. Zircon trace element and isotopic (Sr, Nd, Hf, Pb) effects of assimilation-fractional crystallization of pegmatite magma: A case study of the Guangshigou biotite pegmatites from the North Qinling Orogen, central China[J]. Lithos, 2018, 302-303: 20-36. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2017.12.022
Zagorsky V Y. On emplacement of compositionally heterogeneous pegmatite melts: petrogenetic implications[J]. Estudos Geologicos, 2009, 19(2): 365-369.
Zhang Q C, Liu Y, Wu Z H, et al. Late Triassic granites from the northwestern margin of the Tibetan Plateau, the Dahongliutan example: Petrogenesis and tectonic implications for the evolution of the Kangxiwa Palaeo-Tethys[J]. International Geology Review, 2019, 61(2): 175-194. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2017.1419444
Zhang X, Zhang H, Ma Z L, et al. A new model for the granite–pegmatite genetic relationships in the Kaluan–Azubai–Qiongkuer pegmatite-related ore fields, the Chinese Altay[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2016, 124: 139-155. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.04.020
Zheng Y L, Xu Z Q, Li G W, et al. Genesis of the Markam gneiss dome within the Songpan-Ganzi orogenic belt, eastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Lithos, 2020, 362-363: 105475.
Zhou J S, Wang Q, Xu Y G, et al. Geochronology, petrology, and lithium isotope geochemistry of the Bailongshan granite-pegmatite system, northern Tibet: Implications for the ore-forming potential of pegmatites[J]. Chemical Geology, 2021a, 584: 120484.
Zhou Q F, Qin K Z, Tang D M. Mineralogy of columbite-group minerals from the rare-element pegmatite dykes in the East-Qinling orogen, central China: Implications for formation times and ore genesis[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2021b, 218: 104879.
Zhou Q F, Qin K Z, Tang D M, et al. Mineralogy of Koktokay No. 3 pegmatite, Altai, NW China: implications for evolution and melt-fluid processes of rare-metal pegmatites[J]. European Journal of Mineralogy, 2015, 27(3): 433-457. doi: 10.1127/ejm/2015/0027-2443
Zhu Y F, Zeng Y S, Gu L B. Geochemistry of the rare metal-bearing pegmatite No. 3 vein and related granites in the Keketuohai region, Altay Mountains, northwest China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2006, 27(1): 61-77.



 下载:
下载: