Properties of Pore Air Pressure in Loess During Soaking: Insights from Field Immersion Test
-
摘要:
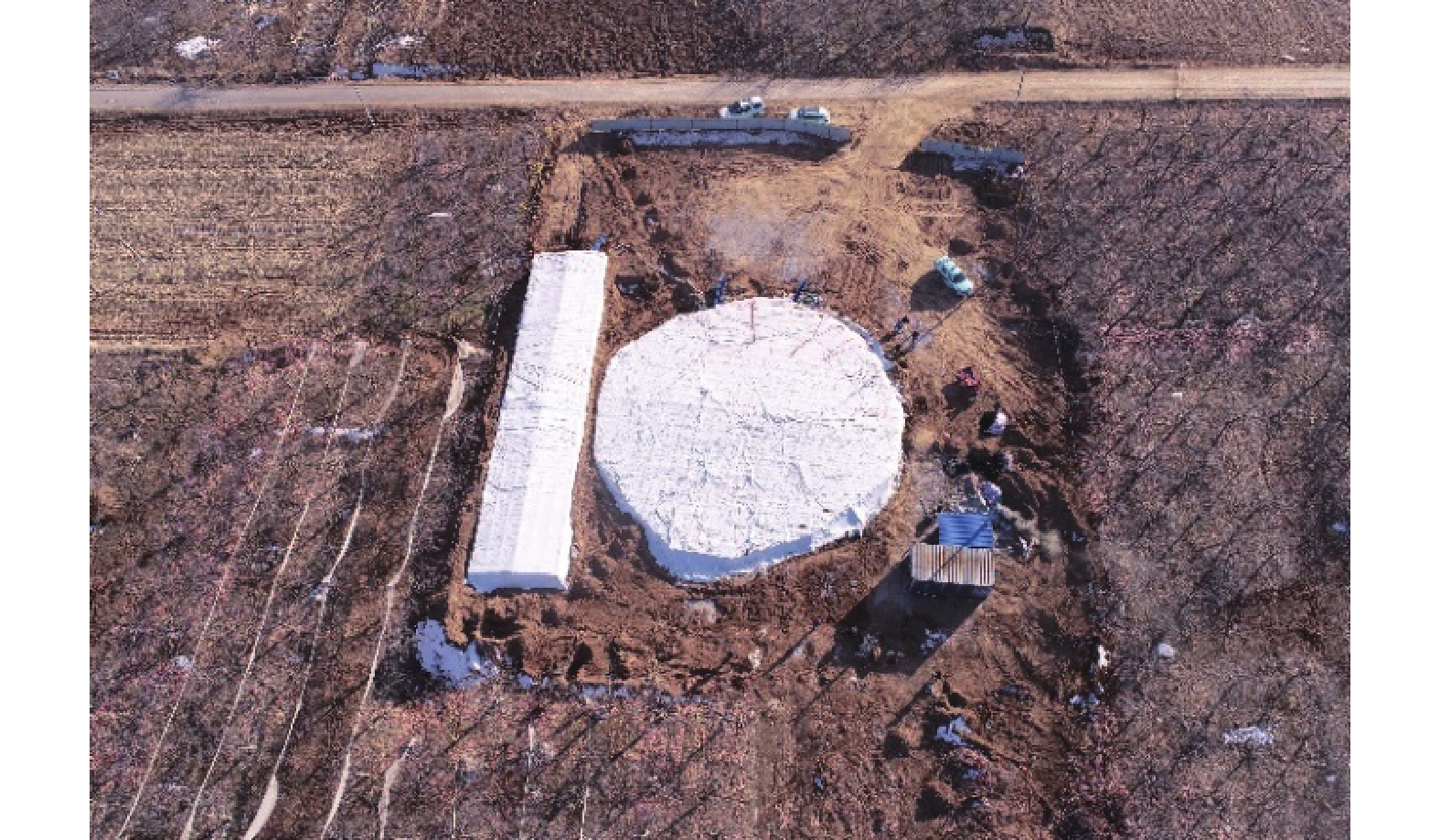
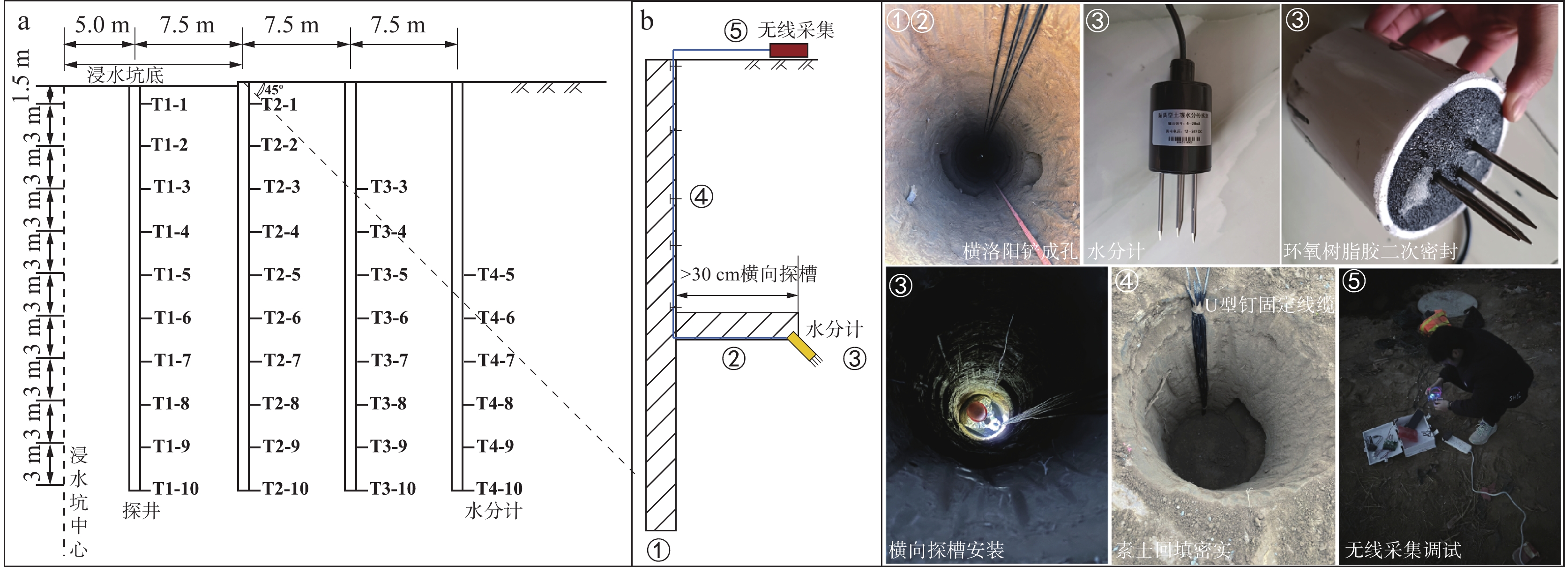
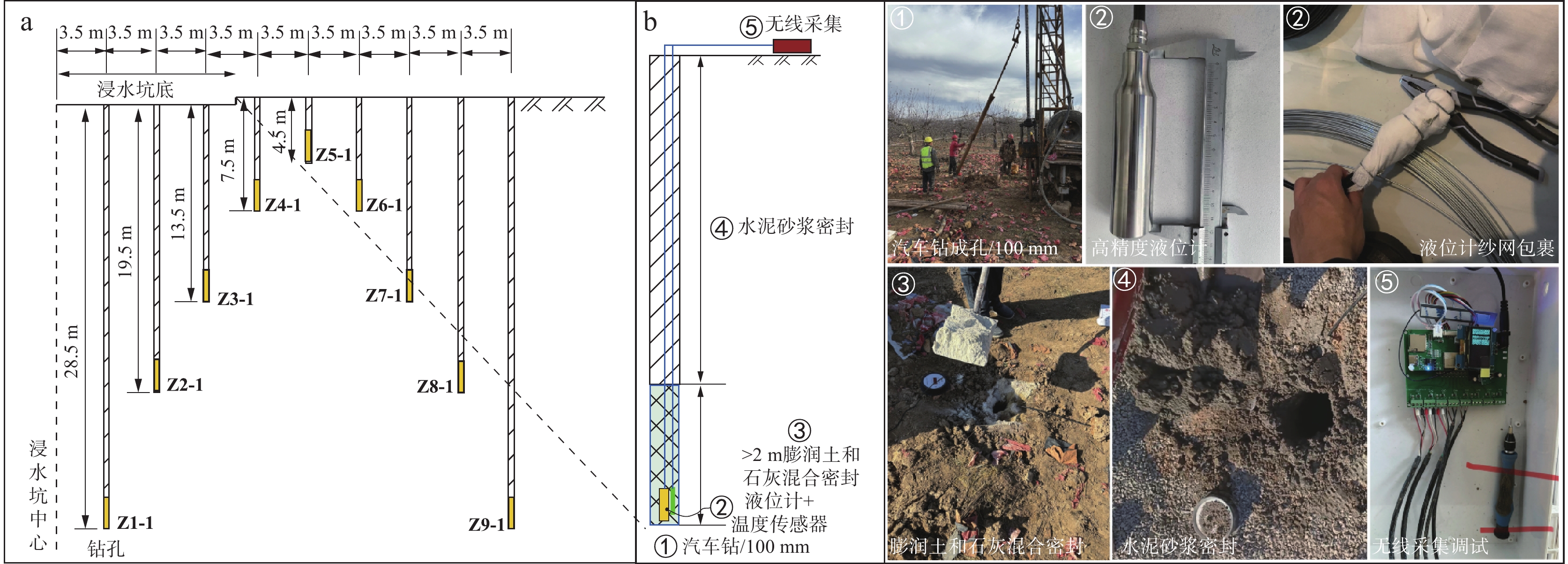
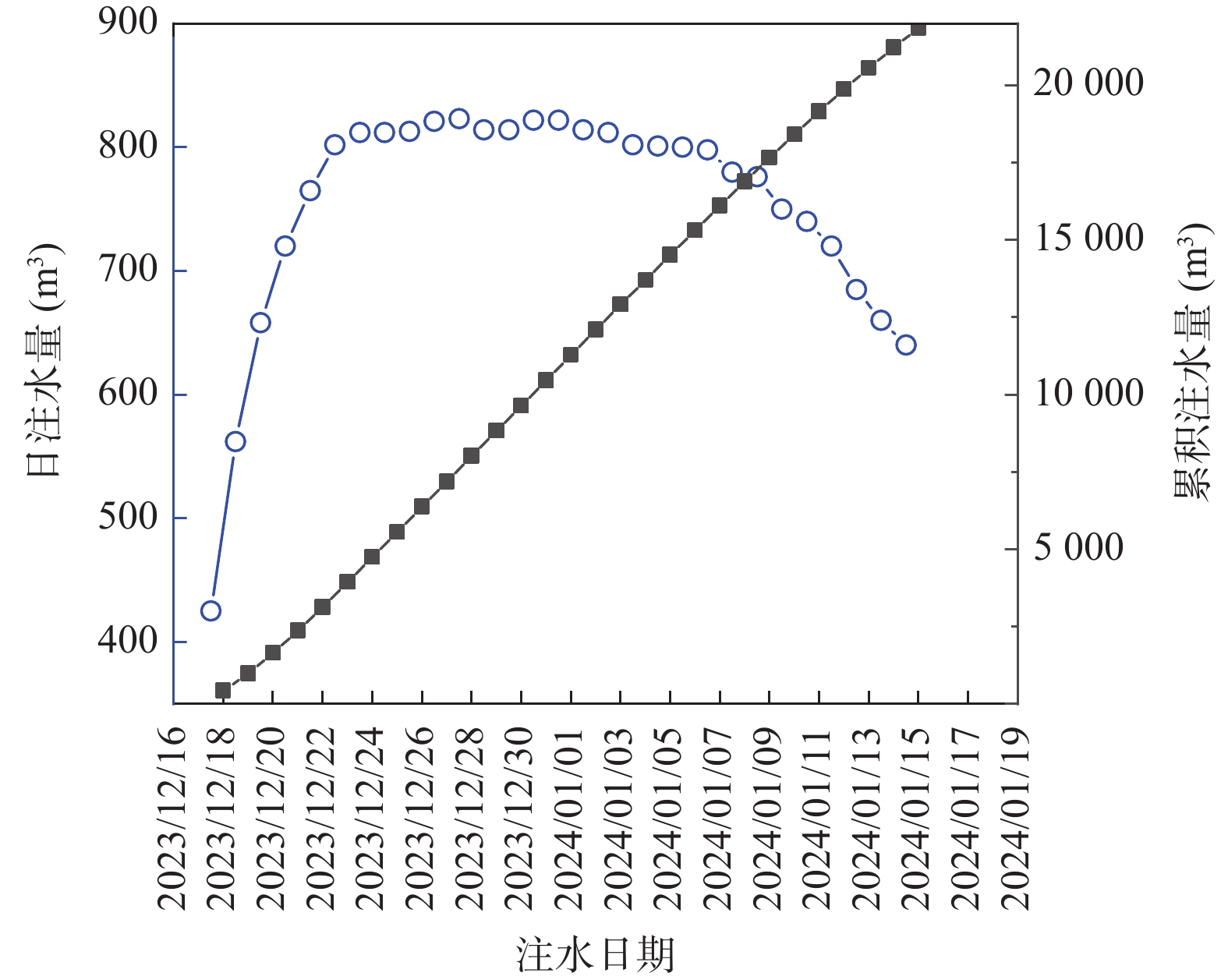
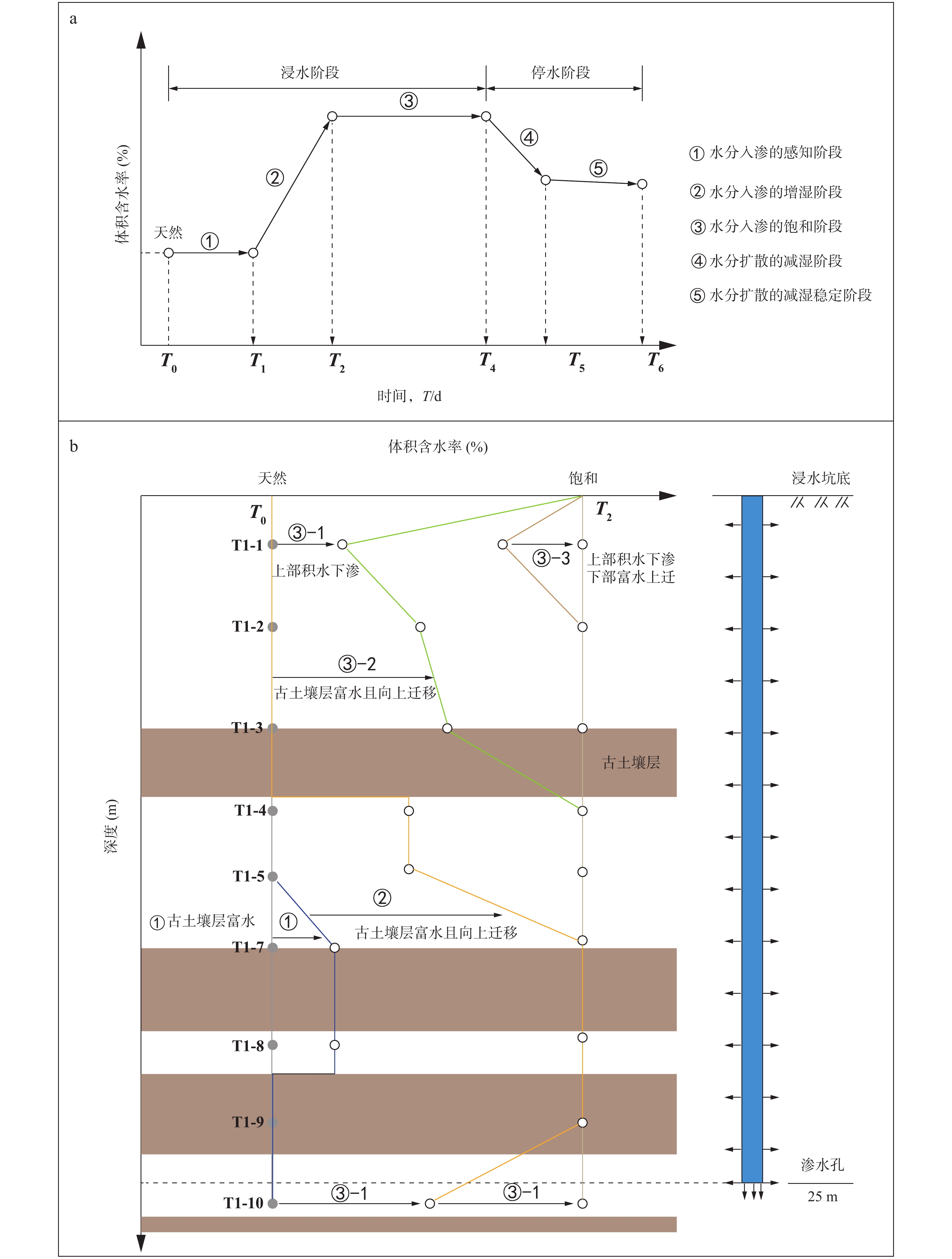
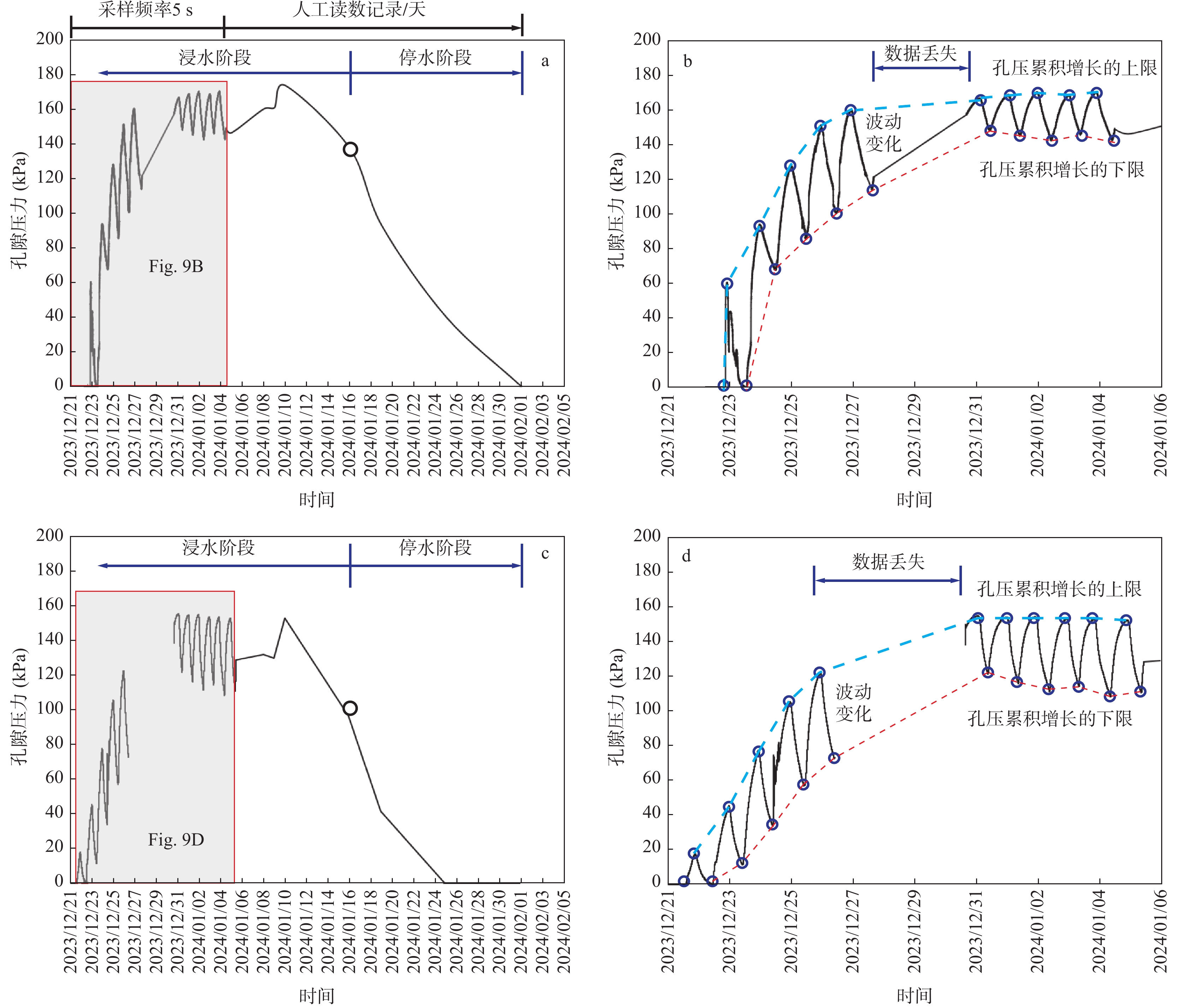
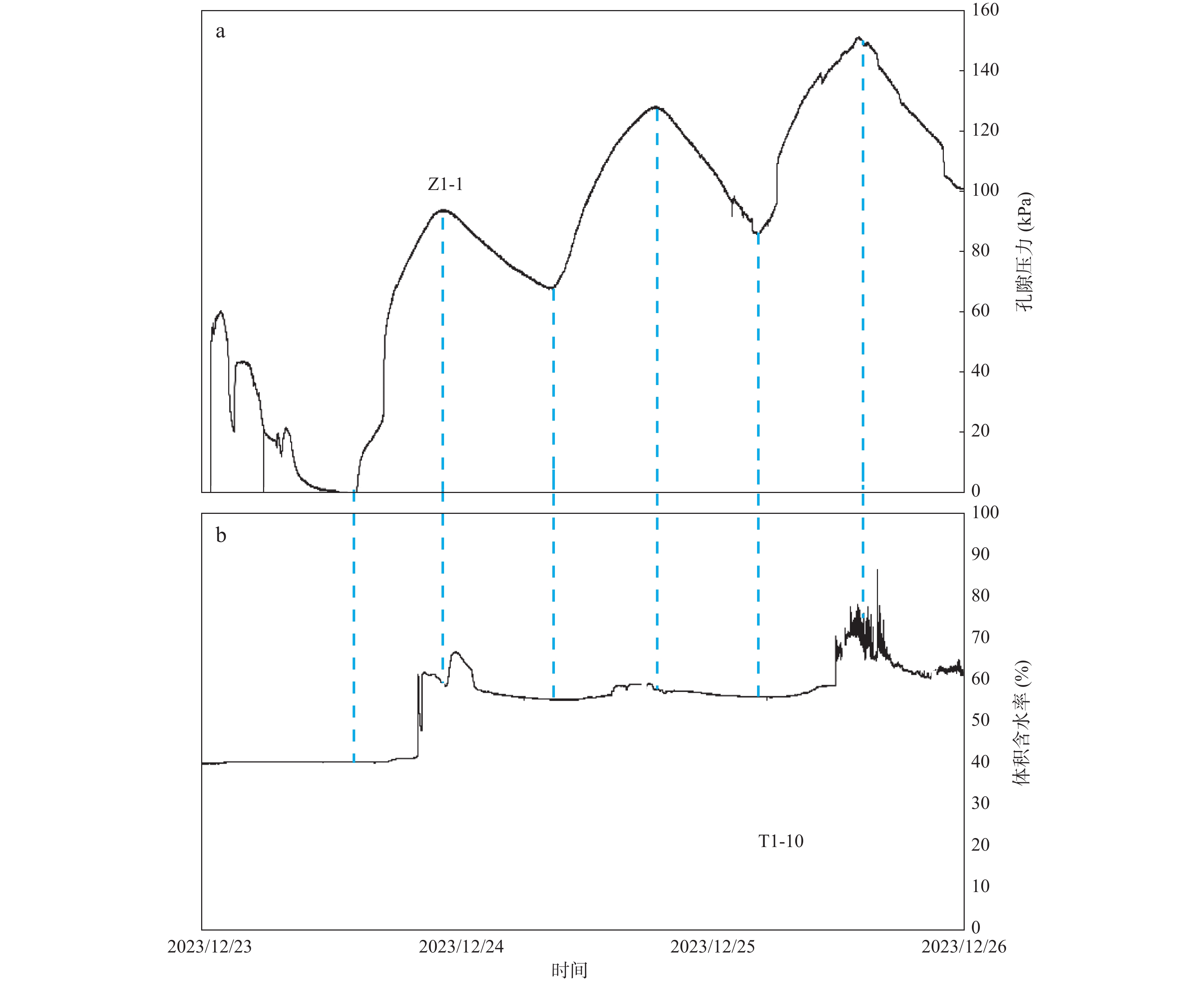
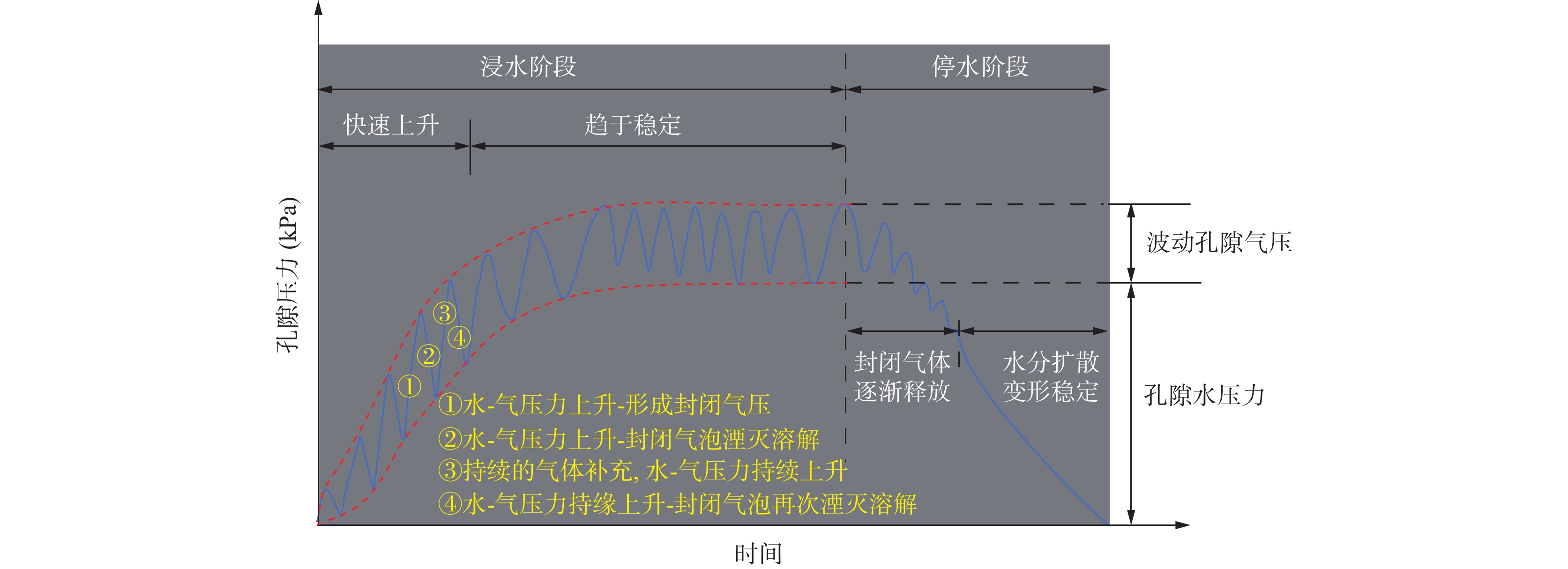
在黄河流域的黄土高原,黄土灾害频发,其关键的地质基因在于对水极为敏感。其中黄土场地遇水后的湿陷变形的科学评价,是黄土灾害研究的主题之一。黄土场地湿陷性逐渐由“最大湿陷势”向“可能湿陷势”转变,迫切需要查明现场试坑浸水试验过程中,黄土中水分入渗–气体迁移–湿陷变形的多场耦合过程。目前,有关现场浸水试验过程中真实测定孔隙气压演化规律鲜有报道。因此,笔者开展黄土高原大厚度自重湿陷性黄土场地现场浸水试坑试验,在典型剖面不同深度布置湿度传感器和孔隙压力传感器,直接测定浸水过程中水分运移和孔隙气体压力,揭示水分运移和气压形成规律。研究结果表明,试坑浸水–停水过程中,呈现出水分入渗的感知–增湿–饱和–减湿–稳定的5阶段变化规律;打设注水孔,明显地改变了试坑中的水分扩散路径,以注水孔的径向渗流——古土壤富水向上迁移的扩散路径为主;首次实现了在大厚度湿陷性黄土大型试坑浸水过程中土体孔隙气压力的原位测定,呈现波动特征,提出了浸水过程中孔隙气压的形成模式。成果为非饱和黄土中水–气运移过程提供实测证据,为进一步精细化预测大厚度黄土的增湿湿陷过程奠定基础。
-
关键词:
- 黄土灾害 /
- 大厚度自重湿陷性黄土 /
- 浸水试验 /
- 水分入渗 /
- 孔隙气压
Abstract:In the Loess Plateau of the Yellow River Basin, loess disasters are frequent, and the key geologic gene is that the loess is extremely sensitivity to water. Among them, the scientific evaluation of wetting-induced collapse deformation of loess site is one of the themes. The wetting-induced collapse deformation of loess site gradually changes from "maximum potential" to "possible potential", and there is an urgent need to find out the multi-field coupling process of water infiltration, gas migration, and wetting-induced collapse deformation in loess during the on-site pit immersion test. At present, there are few reports about the measured pore gas pressure and its evolution law during the on-site pit immersion test. Accordingly, the site immersion test in loess plateau site on large thickness of self-weighted wetted loess were carried out. Moisture sensors and pore pressure sensors were arranged at different depths of typical profiles, to directly measure the water transport and pore gas pressure during the water immersion process, and thus then reveal the water transport and gas pressure formation laws. The results show that the 5-stage change rule of perception of water infiltration - wetting - saturation -drying - stabilization during the on-site pit immersion after stoping. The installation of water injection holes has obviously changed the water diffusion paths in the pit, and the radial seepage from the injection holes and the enrichment of water near paleosoil stratigraphy, whereby resulting in a predominantly upward migration of water. Having realized for the first time, the in-situ measurement of pore gas pressure of the soil during soaking in a large test pit on large thickness of the collapsed loess site. It showed fluctuating changes, and the formation mode of the pore gas pressure during soaking was proposed. The results provided experimental evidence of the coupled water-gas transport in unsaturated loess, and lay the foundation for further refinement of the prediction of the wetting-induced collpase of the large-thickness loess.
-
-
-
胡冉, 陈益峰, 周创兵 . 降雨入渗过程中土质边坡的固-液-气三相耦合分析[J]. 中国科学: 技术科学,2011 ,41 (11 ):1469 −1482 .HU Ran, CHEN Yifeng, ZHOU Chuangbing . Modeling of coupled deformation, water flow and gas transport in soil slopes subjected to rain infiltration[J]. Science China Technological Sciences,2011 ,41 (11 ):1469 −1482 .黄雪峰, 陈正汉, 哈双, 等 . 大厚度自重湿陷性黄土场地湿陷变形特征的大型现场浸水试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2006 ,28 (3 ):382 −389 .HUANG Xuefeng, CHEN Zhenghan, HA Shuang, et al . Large area field immersion tests on characteristics of deformation of self weight collapse loess under overburden pressure[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2006 ,28 (3 ):382 −389 .黄雪峰, 杨校辉 . 湿陷性黄土现场浸水试验研究进展[J]. 岩土力学,2013 (z2 ):222 −228 .HUANG Xuefeng, YANG Xiaohui . A study progress on in-situ soaking test on collapsible loess[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2013 (z2 ):222 −228 .江睿君, 张茂省, 张宇航, 等 . 全吸力范围非饱和黄土土−水特征曲线的一种测试方法[J]. 西北地质,2023 ,56 (3 ):214 −222 .JIANG Ruijun, ZHANG Maosheng, ZHANG Yuhang, et al . A Test Method for Soil−Water Characteristics Curve of Unsaturated Loess in the Full Suction Range[J]. Northwestern Geology,2023 ,56 (3 ):214 −222 .李琳, 王家鼎, 谷琪, 等 . 古土壤层间富水对黄土场地湿陷性的影响[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版),2024 ,54 (1 ):72 −83 .LI Lin, WANG Jiading, GU Qi, et al . The influence of moisture-rich interlayers in palesol strata on the collapsibility of loess terrain[J]. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition),2024 ,54 (1 ):72 −83 .李援农, 费良军 . 土壤空气压力影响下的非饱和入渗格林-安姆特模型[J]. 水利学报,2005 ,36 (6 ):733 −736 .LI Yuannong, FEI Liangjun . Green-Ampt model for unsaturated infiltration affected by air pressure entrapped in soil[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2005 ,36 (6 ):733 −736 .李援农, 吕宏兴, 林性粹 . 土壤人渗过程中空气压力变化规律的研究[J]. 西北农业大学学报,1995 ,23 (6 ):72 −75 .LI Yuannong, LV Hongxing, LIN Xingcui . Regularities of Air Pressure Changes in Soil Infiltration[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-Occidentalis Sinica,1995 ,23 (6 ):72 −75 .刘保健, 谢永利, 于友成 . 黄土非饱和入渗规律原位试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2004 ,23 (24 ):4156 −4160 .LIU Baojian, XIE Yongli, YU Youcheng . In-situ testing study on infiltration in unsaturated loess[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2004 ,23 (24 ):4156 −4160 .刘德仁, 徐硕昌, 洋肖, 等 . 浸水入渗条件下压实黄土水−气运移规律试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2021 ,42 (12 ):3260 −3270 .LIU Deren, XU Shuochang, XIAO Yang, et al . Experimental study on the law of water-air migration in compacted loess under the condition of immersion infiltration[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2021 ,42 (12 ):3260 −3270 .刘颢, 张茂省, 冯立, 等 . 榆林黄河中游粗泥沙区生态问题与生态格局构建[J]. 西北地质,2023 ,56 (3 ):58 −69 .LIU Hao, ZHANG Maosheng, FENG Li, et al . Ecological Problems, Systematically Protection and Restoration Strategies of Yulin Coarse Sand Area in the Middle Yellow River[J]. Northwestern Geology,2023 ,56 (3 ):58 −69 .刘祖典. 黄土力学与工程[M]. 西安: 陕西科学技术出版社, 1997. 马闫. 黄土结构性多尺度研究[D].西安: 西北大学, 2017, 172. MA Yan. Multy scale research of Leoss structural behavior[D]. Xi'an: Northwest University, 2017, 172.
马闫, 王家鼎, 彭淑君, 等 . 大厚度黄土自重湿陷性场地浸水湿陷变形特征研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2014 ,36 (3 ):537 −546 .MA Yan, WANG Jiading, PENG Shujun, et al . Immersion tests on characteristics of deformation of self-weight collapsible loess under overburden pressure[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2014 ,36 (3 ):537 −546 .彭建兵, 兰恒星, 钱会, 等 . 宜居黄河科学构想[J]. 工程地质学报,2020 ,28 (2 ):189 −201 .PENG Jianbing, LAN Hengxing, QIAN Hui, et al . Scientific research framework of livable yellow river[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2020 ,28 (2 ):189 −201 .彭建兵, 林鸿州, 王启耀, 等 . 黄土地质灾害研究中的关键问题与创新思路[J]. 工程地质学报,2014 ,22 (4 ):684 −691 .PENG Jianbing, LIN Hungchou, WANG Qiyao, et al . The critical issues and creative concepts in mitigation research of loess geological hazards[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2014 ,22 (4 ):684 −691 .邵生俊, 李骏, 李国良, 等 . 大厚度自重湿陷黄土湿陷变形评价方法的研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2015 ,37 (6 ):965 −978 .SHAO Shengjun, LI Jun, LI Guoliang, et al . Evaluation method for self-weight collapsible deformation of large thickness loess foundation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2015 ,37 (6 ):965 −978 .邵生俊, 李骏, 邵将, 等 . 大厚度湿陷性黄土地层的现场砂井浸水试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2016 ,38 (9 ):1549 −1558 .SHAO Shengjun, LI Jun, SHAO Shuai, et al . In-situ sand well immersion tests on self-weight collapsible loess site with large depth[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2016 ,38 (9 ):1549 −1558 .孙萍萍, 张茂省, 贾俊, 等 . 中国西部黄土区地质灾害调查研究进展[J]. 西北地质,2022 ,55 (3 ):96 −107 .SUN Pingping, ZHANG Maosheng, JIA Jun, et al . Geo-hazards Research and Investigation in the Loess Regions of Western China[J]. Northwestern Geology,2022 ,55 (3 ):96 −107 .覃小华, 刘东升, 宋强辉, 等 . 降雨条件下一维土柱垂直入渗模型试验研究及其渗透系数求解[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2017 ,36 (2 ):475 −484 .QIN Xiaohua, LIU Dongsheng, SONG Qianghui, et al . Experimental study on one-dimensional vertical infiltration in soil column under rainfall and the derivation of permeability coefficient[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2017 ,36 (2 ):475 −484 .唐海行, 苏逸深, 刘炳敖 . 土壤包气带中气体对人渗水流运动影响的实验研究[J]. 水科学进展,1995 ,6 (4 ):263 −269 .TANG Haixing, SU Yishen, LIU Bingao . Laboratory Study for Influence of Air on the Infiltration Flow in the Soil Unsaturated Zone[J]. Advances in Water Science,1995 ,6 (4 ):263 −269 .汪国烈, 明文山. 湿陷性黄土的浸水、变形规律与工程对策[A]. 湿陷性黄土研究与工程(第四届全国黄土学术会议论文集[C].北京, 2001, 21−32. 王小军, 米维军, 熊治文, 等 . 郑西客运专线黄土地基湿陷性现场浸水试验研究[J]. 铁道学报,2012 ,34 (1 ):83 −90 .WANG Xiaojun, MI Weijun, XIONG Zhiwen, et al . Water Immersion Field Tests of Collapsibility of Loess Foundation of Zhengzhou-Xi'an Passenger Dedicated Line[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society,2012 ,34 (1 ):83 −90 .吴争光, 张华 . 积水入渗稳定时近饱和土中封闭气泡含量试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2012 ,34 (2 ):274 −279 .WU Zhengguang, ZHANG Hua . Experimental study on entrapped air content in quasi-saturated soil subjected to steady ponded water infiltration[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2012 ,34 (2 ):274 −279 .吴爽, 高玉广, 赵权利, 等 . 黄土地场自重湿陷量实测值与计算值差异的原因分析[J]. 西北地质,2019 ,52 (4 ):263 −269 .WU Shuang, GAO Yuguang, ZHAO Quanli, et al . Reason Analysis for the Difference between Measured and Calculated Self-weight Collapsibility of the Loess[J]. Northwestern Geology,2019 ,52 (4 ):263 −269 .武小鹏, 王兰民, 房建宏, 等 . 原状黄土地基渗水特性及其与自重湿陷的关系研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2018 ,40 (6 ):1002 −1010 .WU Xiaopeng, WANG Lanmin, FANG Jianhong, et al . Seepage characteristics andtheir relationship with self-weight collapse of intact loess ground[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2018 ,40 (6 ):1002 −1010 .谢定义 . 黄土力学特性与应用研究的过去、现在与未来[J]. 地下空间,1999 ,19 (4 ):273 −284+338 .XIE Dingyi . The past, present and future of the research on mechanical characteristics and application of Loess[J]. Underground Space,1999 ,19 (4 ):273 −284+338 .谢定义, 邢义川. 黄土土力学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2016. 姚志华, 黄雪峰, 陈正汉, 等 . 兰州地区大厚度自重湿陷性黄土场地浸水试验综合观测研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2012 ,34 (1 ):65 −74 .YAO Zhihua, HUANG Xuefeng, CHEN Zhenghan, et al . Comprehensive soaking tests on self-weight collapse loess with heavy section in Lanzhou region[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2012 ,34 (1 ):65 −74 .张爱军, 邢义川, 汪海涛, 等 . 基于增湿变形的渠道工程黄土渠基湿陷性评价方法[J]. 水利学报,2017 ,48 (1 ):41 −51+60 .ZHANG Aijun, XING Yichuan, WANG Haitao, et al . Evaluation method for collapsibility of channel engineering with Loess foundation based on moistening deformation[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2017 ,48 (1 ):41 −51+60 .张贡生 . 黄河经济带建设: 意义、可行性及路径选择[J]. 经济问题,2019 ,(7 ):123 −129 .ZHANG GongSheng . Construction of the Yellow River Economic Belt: Significance, Feasibility and Path Selection[J]. On Economic Problems,2019 ,(7 ):123 −129 .张林, 张登飞, 陈存礼, 等 . 竖向压力作用下重塑黄土土柱压缩湿陷及渗水试验研究[J]. 水利学报,2019 ,50 (10 ):1214 −1221 .ZHANG Lin, ZHANG Dengfei, CHEN Cunli, et al . Experimental study on compression collapsibility and infiltration of remolded loess soil column under vertical pressure[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2019 ,50 (10 ):1214 −1221 .郑建国, 邓国华, 刘争宏, 等 . 黄土湿陷性分布不连续对湿陷变形的影响研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2015 ,37 (1 ):165 −170 .ZHENG Jianguo, DENG Guohua, LIU Zhenghong, et al . Influence of discontinuous distribution of collapsible loess on its deformation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2015 ,37 (1 ):165 −170 .Wang Z, Feyen J, van Genuchten M T, et al . Air entrapment effects on infiltration rate and flow instability[J]. Water Resources Research,1998 ,34 (2 ):213 −222 .Wu L Z, Selvadurai A P S, Zhang L M, et al . Poro-mechanical coupling influences on potential for rainfall-induced shallow landslides in unsaturated soils[J]. Advances in Water Resources,2016 ,98 :114 −121 .Yao Z, Chen Z, Fang X, et al . Elastoplastic damage seepage–consolidation coupled model of unsaturated undisturbed loess and its application[J]. Acta Geotechnica,2020 ,15 (6 ):1637 −1653 .




 下载:
下载: