Dynamic Evolution of Eco−geological Pattern: Taking Danjiangyuan Area of Central Line Project of South−to−North Water Diversion
-
摘要:
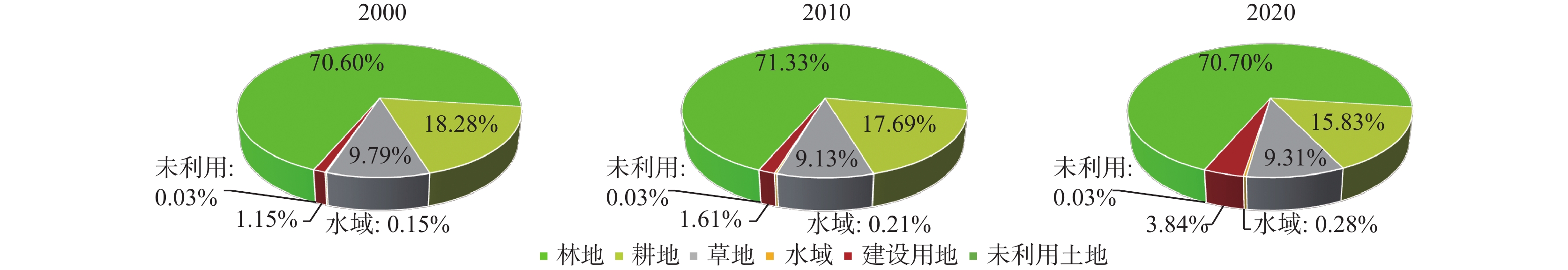
以南水北调中线工程水源涵养区丹江源地区为研究区,采用坡面调查方法,梳理不同地质建造上的典型生态关键带生态地质特征,利用ENVI 5. 3、ArcGIS 10.2及Fragstats4.2软件,解译分析区内2000、2010、2020年3期土地利用时空演变和景观格局演变特征。结果表明:①受构造地质背景影响,各地质建造垂向上形成不同的地形地貌、成土母质、土壤类型、水文类型,在以上立地条件的综合影响下形成了不同的生态地质格局。②区内林地比例占绝对优势,林地和耕地占比85%以上,其他土地类型比例偏低。2000~2020年土地利用类型变化显著,水域、耕地和建设用地面积变化较为剧烈。区内自然景观和人造景观之间转入转出频繁,但整体土地利用变化对生态环境扰动较少。林地和耕地将长期是水源地主要的土地利用类型,直接影响着其生态环境效应。③丹江源地区2000~2020年景观空间格局变化明显,尤其在2010~2020年景观生态过程较活跃。区内各斑块类型趋于规则呈均衡趋势分布,斑块类型间形成了良好的连接性,景观聚集程度逐渐提升,空间分布趋向集中。④南水北调中线工程建设进一步保障了研究区林地基数和水域面积的稳定增长,丹江源地区的生态趋势向好;调水工程及城市化进程建设及保护水源地的移民搬迁导致区内建设用地大幅度增加,存在草地退化和耕地减少现象。建议合理配置土地资源,优化土地利用结构,加强林地和耕地保护及生态补偿,将有利于丹江源地区社会经济和生态环境的可持续发展。
Abstract:Taking Danjiangyuan area of central line project of south–to–north water diversion as the research area, the eco–geological characteristics of typical eco–critical zones in different geological formation were combed by slope survey. This paper extracts remote sensing data from 2000 to 2020 to interpret land use types and analyze the spatial and temporal evolution of land use and the evolution characteristics of landscape pattern with the help of ENVI 5.3, ArcGIS 10.2 and Fragstats4.2 software. The results show that each geological formation forms different landforms, soil parent material, soil types and hydrological types in vertical influenced by the structural geology setting. Different eco–geological patterns have been formed under the comprehensive influence of the above site conditions. The proportion of forest land is absolutely dominant, with forest land and arable land accounting for more than 85%, while the proportion of other land types is low. The types of land use changed significantly from the year of 2000 to 2020. Water area, cultivated land and construction land have changed dramatically. There are frequent transfers between natural landscapes and artificial landscapes in the area, and land use changes have less disturbance to the ecological environment. Forest and cultivated land are the main land use types of water source land for a long time, which directly affect their ecological and environmental effects. From 2000 to 2020, the landscape spatial pattern changed significantly, especially from 2010 to 2020, the landscape ecological process was more active. The patch types in the area tend to be distributed regularly and in a balanced trend, with good connectivity between patch types, the degree of landscape aggregation gradually increases, and the spatial distribution tends to be concentrated. The construction of central line project of south–to–north water diversion has further guaranteed the stable growth of the forest land base and water area in the study area, and the ecological trend in Danjiangyuan area is improving. Water transfer projects, urbanization construction and resettlement of protected water source areas have resulted in a substantial increase in construction land in the area, with grassland degradation and arable land reduction. It is suggested that rational allocation of land resources, optimization of land use structure, strengthening of forest land and cultivated land protection and ecological compensation will be conducive to the sustainable development of social economy and ecological environment in Danjiangyuan area.
-
Keywords:
- water conservation area /
- Danjiangyuan area /
- eco–geology /
- land use change /
- landscape pattern
-
-
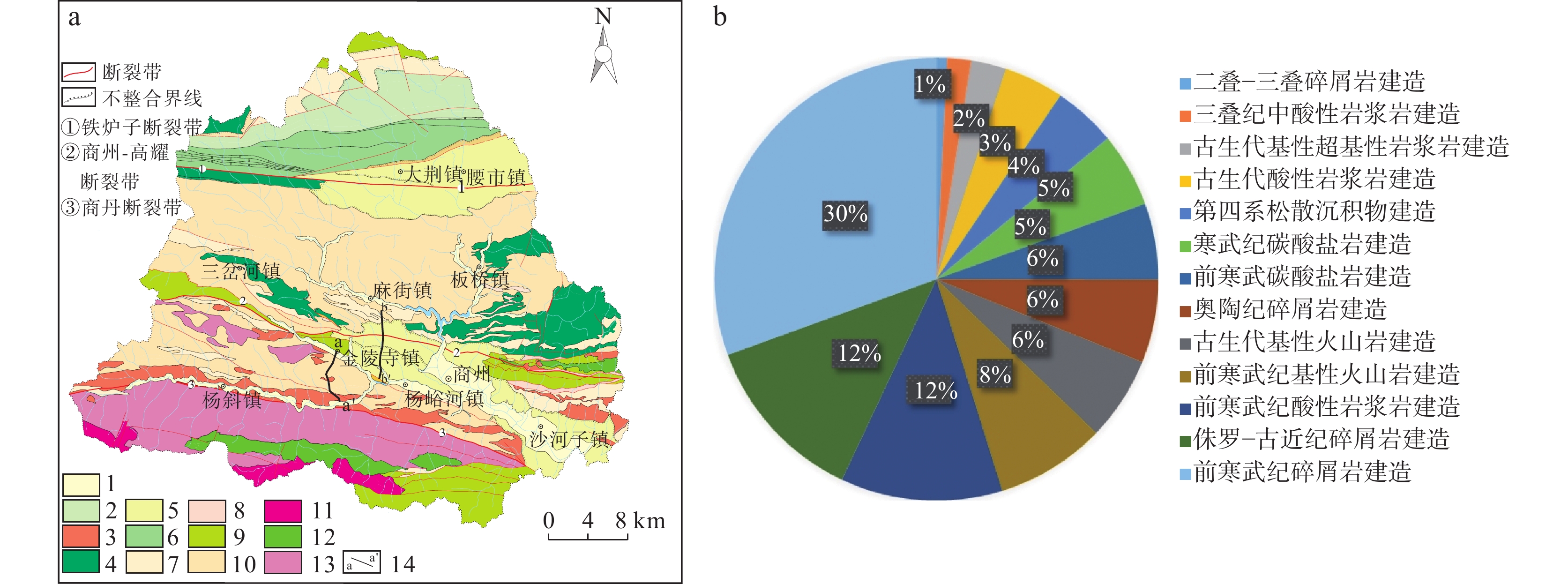
图 2 丹江源地区地质建造图(a)及不同地质建造面积分布图(b)
1.第四纪陆相松散堆积建造;2.寒武纪海相碳酸盐岩建造;3.古生代中酸性岩浆岩建造;4.寒武纪基性火山岩建造;5.侏罗纪-古近纪陆相砂泥质碎屑岩建造;6.奥陶纪泥质碎屑岩建造;7.前寒武纪碳酸盐岩建造;8.三叠纪陆相砂泥质碎屑岩建造;9.古生代基性火山岩建造;10.前寒武纪砂泥质碎屑岩建造;11.三叠纪中酸性岩浆岩建造;12.古生代基性-超基性岩浆岩建造;13.前寒武纪酸性岩浆岩建造;14.实测剖面
Figure 2. (a) Geological construction map and (b) distribution map of different geological construction areas in Danjiangyuan area
表 1 景观格局指数选取及指示意义
Table 1 Selection and indicative significance of landscape pattern index
景观单元特征指数 指标选取 指示意义 景观面积度量指标 斑块类型面积(CA) CA值的大小影响着斑块类型聚集地中的物种数量及丰度 斑块类型比(PLAND) PLAND指某一斑块类型占整个景观面积的相对比例 最大斑块指数(LPI) LPI主要表示某一景观类型最大斑块占整个景观面积的比例,决定了景观优劣斑块,反应景观变化受人类活动干扰程度 景观面积(TA) TA定义景观幅度,是监测生态系统是否稳定的重要指标 景观形状指标 景观形状指数(LSI) LSI反映景观和斑块形状的分散和规则程度,值越大说明景观形状越复杂 景观邻近度指标 香农多样性指数(SHDI) SHDI表示景观类型的复杂程度,值越小斑块类型越少,值增大说明斑块类型增加或各斑块类型在景观中呈均衡化趋势分布 景观聚集与分散度
测量指标蔓延度指数(CONTAG) CONTAG反映景观类型的聚集程度和延展程度,高蔓延度值表明某种优势斑块类型具有良好的连通性 散布与并列指数(IJI) IJI反映斑块类型的隔离分布情况 聚集度指数(AI) AI是基于栅格数量来测度景观或者某种斑块类型的聚集程度 注:各景观格局指数计算公式和详细意义可参阅相关文献(何鹏等,2009;孙天成等,2019)。 表 2 丹江源地区2000~2020年土地动态度变化
Table 2 Changes of land dynamic attitude from 2000 to 2020 in Danjiangyuan area
土地利用类型土地动态度 2000~2010年 2010~2020年 2000~2020年 耕地
林地
草地
水域
建设用地
未利用土地−0.32%
0.10%
−0.67%
3.54%
3.98%
−0.08%−1.05%
−0.09%
0.20%
3.66%
13.89%
0.07%−0.67%
0.01%
−0.24%
8.51%
11.70%
−0.05%表 3 丹江源地区2010~2020年3期斑块类型水平的景观格局指数
Table 3 Landscape pattern indices of patch types in the Danjiangyuan area from 2010 to 2020
斑块类型 年份 CA(km2) PLAND(%) LPI(%) LSI IJI AI 林地 2000 1240.4300 76.0300 72.6400 17.4570 39.6831 98.0450 2010 1253.2700 75.8700 72.4600 17.6510 34.3240 98.0204 2020
20001242.2100
321.120075.1900
20.810071.4900 16.8271 37.6794 98.1100
88.0625耕地 20.2100 53.5204 53.9354 2010 310.8700 21.0200 20.4700 53.1127 47.0259 88.2095 2020 278.1700 20.8100 17.1600 57.3163 48.3957 87.2000 草地 2000 171.9900 2.7400 0.1900 84.8531 28.3333 47.1916 2010 160.3900 2.5300 0.0500 85.8279 23.7656 44.2992 2020 163.6400 2.7500 0.0500 95.8660 19.9750 40.3615 水域 2000 2.6800 0.0400 0.0300 8.1220 71.1135 62.7075 2010 3.6300 0.0600 0.0400 6.5652 62.6626 73.7705 2020 4.9600 0.0800 0.0700 6.7037 72.2046 77.8098 建设用地 2000 20.1800 0.3400 0.1000 12.7699 47.8730 78.5033 2010 28.2200 0.4700 0.1400 13.2256 42.9460 81.0820 2020 67.4100 1.1300 0.8000 14.8398 49.5618 86.4070 未利用土地 2000 0.4700 0.0400 0.0800 2.1938 31.5743 38.8427 2010 0.5000 0.0500 0.0900 2.7472 32.2674 39.3754 2020 0.4900 0.0400 0.0800 2.3584 31.6832 38.7120 注:由于各土地利用类型斑块类型面积统计存在四舍五入,面积总和与研究区总面积有略微出入。 表 4 丹江源地区2000~2020年景观水平的景观格局指数
Table 4 Landscape pattern index of the Danjiangyuan area from 2000 to 2020
年份 TA(km2) LSI CONTAG IJI SHDI AI 2000 1757.0000 27.8229 73.2957 45.5026 0.6557 94.4950 2010 1757.0000 27.7720 75.9058 39.2190 0.6596 94.5070 2020 1757.0000 29.7378 74.7040 40.4132 0.6963 94.1028 注:TA. 景观面积;LSl. 景观形状指数;CONTAG. 蔓延度指数;IJI. 散布与并列指数;SHDI. 香农多样性指数;Al. 聚集度指数。 -
陈利顶, 刘洋, 吕一河, 等. 景观生态学中的格局分析: 现状、困境与未来[J]. 生态学报, 2008, (11): 5521-5531 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2008.11.037 CHEN Liding, LIU Yang, LÜ Yihe, et al. Landscape pattern analysis in landscape ecology: current, challenges and future[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2008, (11): 5521-5531. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2008.11.037
陈利顶, 孙然好, 刘海莲. 城市景观格局演变的生态环境效应研究进展[J]. 生态学报, 2013, 33(4): 1042⁃ 1050. CHEN Liding, SUN Ranhao, LIU Hailian. Eco-environmental effects of urban landscape pattern changes: progress’ problems’ and perspectives[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2013, 33(4): 1042-1050 .
陈文波, 肖笃宁, 李秀珍. 景观指数分类、应用及构建研究[J]. 应用生态学报, 2002, 13(01): 121-125 CHEN Wenbo, XIAO Duning, LI Xiuzhen. Classification, application, and creation of landscape indices[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology. 2002, 13(01): 121-125.
中国科学院计算机网络信息中心科学数据中心. 地理空间数据[DB]. 地理空间数据云官网. http://www.gscloud.cn 国家气象科学数据中心. 中国地面气候资料月值数据集[DB]. 国家气象科学数据中心, 1951−2020. 何鹏, 张会儒. 常用景观指数的因子分析和筛选方法研究[J]. 林业科学研究, 2009, 22(04): 470-474 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1498.2009.04.002 HE Peng, ZHANG Huiru. Study on factor analysis and selection of common landscape metrics[J]. Forest Research, 2009, 22(04): 470-474. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-1498.2009.04.002
李文明, 李健强, 徐永, 等. 西北生态地质调查研究进展与展望[J]. 西北地质, 2022, 55(03): 108-119 LI Wenming, LI Jianqiang, XU Yong, LIU Tuo, et al. Progress and Prospects of Ecological Geological Survey in Northwest China [J]. Northwestern Geology, 2022, 55(03): 108-119.
李煜东, 臧传富, 陈相龙. 淮河流域 1990-2015年间土地利用时空变化特征及驱动机制研究[J]. 生态科学, 2020, 39(02): 104-113 LI Yudong, ZANG Chuanfu, CHEN Xianglong. Research on temporal and spatial variation characteristics and driving mechanism of land use in Huaihe River Basin from 1990 to 2015[J]. Ecological Science, 2020, 39(02): 104–113.
聂洪峰, 肖春蕾, 戴蒙, 等. 生态地质调查工程进展与主要成果[J]. 中国地质调查, 2021, 8(01): 1-12 doi: 10.19388/j.zgdzdc.2021.01.01 NIE Hongfeng, XIAO Chunlei, DAI Meng, et al. Progresses and main achievements of ecological survey project[J]. Geological Survey of China, 2021, 8(01): 1-12. doi: 10.19388/j.zgdzdc.2021.01.01
潘贤章, 施建平. 全国第二次土壤普查典型土种的剖面数据库(1980-1996)[DB]. 国家地球系统科学数据共享平台-土壤科学数据中心, 2015 陕西师范大学地理系. 陕西省商洛地区地理志[M]. 西安: 陕西人民出版社. 1981. Department of Geography, Shaanxi Normal University. Geography of Shangluo, Shaanxi Province [M]. Xi’an: Shaanxi People’s Publishing House, 1981.
苏明伟, 张伟峰, 杜鹃, 等. 2010-2018年陕西省LUCC动态变化分析[J]. 湖北农业科学, 2021, 60(05): 29-34 SU Mingwei, ZHANG Weifeng, DU Juan, et al. Analysis on the dynamic changes of LUCC in Shaanxi province from 2010 to 2018[J]. Hubei Agricultural Sciences, , 2021, 60(05): 29-34.
孙天成, 刘婷婷, 褚琳, 等. 三峡库区典型流域“源”“汇”景观格局时空变化对侵蚀产沙的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2019, 39(20): 7476-7492 SUN Tiancheng, LIU Tingting, CHU Lin, et al. Effects of temporal and spatial variations in source-sink landscape patterns on soil erosion and sediment yield from typical watershed in the Three Gorges Reservoir area, China[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinca, 2019, 39(20): 7476-7492.
王京彬, 卫晓锋, 张会琼, 等. 基于地质建造的生态地质调查方法-以河北省承德市国家生态文明示范区综合地质调查为例[J]. 中国地质, 2020, 47(06): 1611-1624 WANG Jingbin, WEI Xiaofeng, ZHANG Huixiong, et al. The eco-geological survey based on geological formation, exemplified by integrated geological survey of National Ecological Civilization Demonstration Area in Chengde City, Hebei Province[J]. Geology in China, 2020, 47(06): 1611-1624.
王天山, 郑寒. 城市化过程中环洱海区域土地利用及景观格局变化分析[J]. 生态经济, 2016, 32(01); 181-185. WANG Tianshan, ZHEGN Han. Analysis of land use and landscape pattern change in Erhai lake during rapid urbanization[J]. Ecological economy, 2016, 32(01): 181-185.
王尧, 张茂省, 杨建锋. 中国地质环境脆弱性评价[J]. 西北地质, 2019, 52(02): 198-206 WANG Yao, ZHANG Maosheng, YANG Jianfeng. Evaluation Research on the Fragility of Geological Environment in China[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2019, 52(2): 198-206.
邬建国. 景观生态学: 格局、过程、尺度与等级[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2000 WU Jianguo. Landscape ecology: pattern, process, scale and hierarchy[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2000
岳德鹏, 王计平, 刘永兵, 等. GIS与RS技术支持下的北京西北地区景观格局优化[J]. 地理学报, 2007, (11): 1223-1231 YUE Depeng, WANG Jiping, LIU Yongbing, et al. , Landscape pattern optimization based on RS and GIS in northwest of beijing[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2007, (11): 1223-1231.
张建, 雷刚, 漆良华, 等. 2003-2018年土地利用变化对丹江口市景观格局与生态服务价值的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2021, 41(04): 1280-1290 ZHANG Jian, LEI Gang, Qi Lianghua, , et al. The landscape pattern and ecological service value in Danjiangkou City under land use change from 2003 to 2018. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2021, 41(04): 1280-1290.
张林, 李来新, 马东民, 等. 景观格局及生态系统服务价值响应-以千阳县为例[J]. 西北地质, 2022, 55(01): 274-283 ZHANG Lin, LI Laixin, MA Dongmin, et al. On the Landscape Pettern Change and the Ecological Service Value Response: Taking Qianyang County as an Example[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2022, 55(01): 274-283.
张茂省, 王尧, 薛强. 资源环境承载力评价理论方法与实践[J]. 西北地质, 2019, 52(02): 1-11 ZHANG Maosheng, WANG Yao, XUE Qiang. Evaluation of Resource Environment Carrying Capacity: Theoretical Method and Practice[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2019, 52(2): 1-11.
张晓宁, 刘学录, 王全喜, 等. 盐池县土地利用自然生态位变化及其对景观格局的影响[J]. 生态科学, 2020, 39(01): 156-163 ZHANG Xiaoning, LIU Xuelu, WANG Quanxi, et al. The change of natural niche of land use and its influence on landscape pattern of Yanchi County[J]. Ecological Science, 2020, 39(01): 156-163.
张雁, 李占斌, 刘建林. 南水北调中线商洛水源地生态安全评价[J]. 人民长江, 2016, 47(19): 32-36 ZHANG Yan, LI Zhanbin, LIU Jianlin. Ecological safety assessment on Shangluo water area of Middle Route Project of South-to-North Water Diversion [J]. Yangtze River, 2016, 47(19): 32-36.
张雁. 山区水源地建设的生态环境效应评价与保护研究[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2018 ZHANG Yan. Ecological environmental assessment and protection of water source construction projects in mountainous area: a case study in Shagnluo water source area[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Technology, 2018.
CHEN Fei, CHEN Jun, and WU Hao, et al. 2016. A landscape shape index-based sampling approach for land cover accuracy assessment[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 2016, 59: 2263-2274. doi: 10.1007/s11430-015-5280-5
CHEN Jin, ZHU Xiaolin, and Vogelmann James E. , et al. A simple and effective method for filling gaps in Landsat ETM SLC-off images[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2011, 115(4): 1053-1064. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2010.12.010
CHEN Jun, BAN Yifang, LI Songnian. China: Open access to Earth land-cover map[J]. Nature, 2014, 514(7523): 434-434.
Moser D, Zechmeister H G, Plutzar C, et al. Landscape patch shape complexity as an effective measure for plant species richness in rural landscapes[J]. Landscape Ecology, 2002, 17(7): 657-669.
Robert Costanza. Ecological Economies: reintegrating the study of humans and nature[J]. Nature Sciences Société, 1997, 5(2): 90
Veldkamp A, Verburg P H. Modelling land use change and environmental impact[J]. Journal of Environmental Management, 2004, 72(1-2S1): 1-3.
ZHU Xiaolin, CHEN Jin, and Gao Feng, et al. An enhanced spatial and temporal adaptive reflectance fusion model for complex heterogeneous regions[J]. Remote Sensing of Environment, 2010, 114(11): 2610-2623. doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2010.05.032



 下载:
下载: